Overview of the significantly regulated pathways and TFs during somitogenesis under Msgn1 overexpression
According to our GSEA of the data sets of 18 samples used in the microarray experiment by the comparison of Msgn1 overexpression to wild-type mice, there were 100 significantly associated pathways identified with p < 0.01 at 12h, including 83 upregulated and 17 downregulated pathways. Moreover, there were 113 significant pathways including 29 upregulated and 84 downregulated ones at 24h, as well as 183 significant pathways including 50 upregulated and 113 downregulated ones at 48h. The details of each pathway are given in Table S-1. In order to predict TFs potentially involved in embryonic stem cell differentiation in the case of Msgn1 overexpression, we implemented the analysis of TFBSs and the prediction of TFs using the significant genes in each identified pathway. Based on the cutoff value of TF importance, we have identified the associated TFs with potential target genes that are co-regulated in each of the above-mentioned 376 pathways. The details are shown in Table S-2.
To further explain the regulatory mechanism of Msgn1 functions in the process of embryonic stem cells development, we have further combined the related ChIP-seq results with our GSEA target genes in different developmental stages, which were shown in Figure 1. As a result, there were 356 common genes identified at 12h, 362 common genes at 24h and 484 common genes at 48h. The details of common genes are shown in Table S-3.
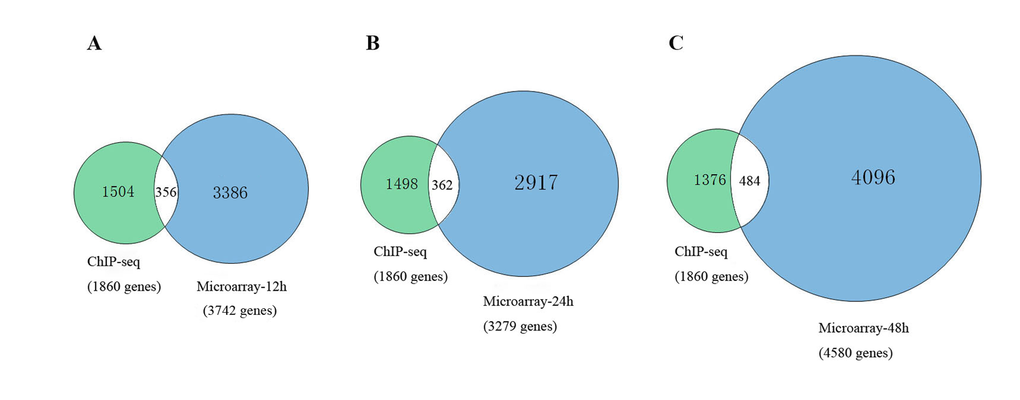
Figure 1. The comparison between related ChIP-seq results with our GSEA target genes.
Specific signaling pathways during somitogenesis under Msgn1 overexpression
Based on the GSEA approach, we have identified several significantly related pathways during somitogenesis in mice. By the comparison of each group, we have further identified 39 overlapping pathways significantly regulated in these three periods, including 8 signaling pathways (Figure 2). Most of these signaling pathways are related to immune system (3/8) and signal transduction (4/8) according to KEGG pathway maps in the KEGG database (http://www.genome.jp/kegg/). We next screened and reorganized the entire signaling pathways at three time points, the details of which were showed in Table S-4 and Table S-5. Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway is only significantly regulated in 12h, which belongs to the immune system. There are 2 specific signaling pathways significantly regulated in 24h, PPAR signaling pathway and Insulin signaling pathway, and both of them are concerned with the endocrine system. Similarly, there are 2 signaling pathways significantly regulated in 48h: Jak-STAT signaling pathway which is correlated with signal transduction and B cell receptor signaling pathway which is correlated with the immune system. Moreover, 2 signaling pathways play roles at both 12h and 24h, which are related to the nervous system and signal transduction respectively. In addition, 3 signaling pathways are regulated significantly at 12h and 48h. Among them, VEGF signaling pathway is related to the signal transduction, while Toll-like receptor signaling pathway and NOD-like receptor signaling pathway are belong to the immune system. In 24h and 48h overlapping signaling pathways, 3 signaling pathways functioned in the signal transduction while the other 2 signaling pathways act in the endocrine system.
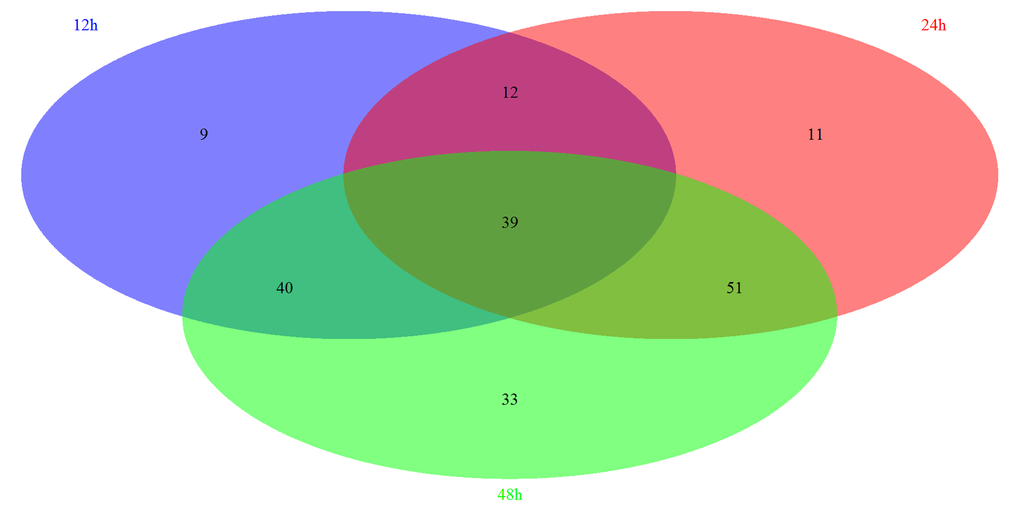
Figure 2. The summary of significantly regulated pathways based on GSEA under Msgn1 overexpression. The Venn diagram showed the comparisons of each time point. There are 100 most significant pathways at 12 hour, 113 significant pathways at 24 hour and 163 significant pathways at 48 hour. By the comparison of 3 different time points, 39 significantly associated pathways were overlapped. By the comparison of 12h and 24h time points, 51 significant pathways were overlapped. Similarly, 79 and 90 overlapping significant pathways were identified respectively while comparing between 12h and 48h, between 24h and 48h.
According to Table 1, most signaling pathways are concerned with signal transduction (10/23) such as MAPK signaling pathway, Hedgehog signaling pathway and mTOR signaling pathway. Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) signal is one of the important ways in the eukaryotic cell, which adjusts and controls the structure and function of the cell. MAPKs play a vital role in the production of matrix metalloproteinases and the regulation of cartilage cell proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation [17]. The Hedgehog pathway is a key signaling pathway controlling key steps of embryonic development and patterning through the early stages of development as well as in the development of most tissues and organs in mammals [18,19]. MTOR is a core protein in early embryo development, which highlights the dynamic role of TOR signaling and presents additional functions beyond cell growth control during embryonic development [20]. In addition, some other signaling pathways like RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway and Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway regulate in the immune system (7/23). The RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway can help create the ability to recognize virus infection and to enhance a powerful antiviral response, which plays an important role in immune systems. RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway can activate the production of antiviral cytokines and the establishment of an effective cellular antiviral state by triggering signal transduction pathways, which preserves neighboring cells against infection and initiates native and adaptive immune systems [21[.
Table 1. The summary of gene expression datasets
| Series | Contributor | Platform | Design | Replicates |
| Time Points | Treatment |
| GSE29848 | Chalamalasetty et al. | Affymetrix Mouse Genome 430 2.0 Array | 12h | MinDox | 3 |
| PlusDox | 3 |
| 24h | MinDox | 3 |
| PlusDox | 3 |
| 48h | MinDox | 3 |
| PlusDox | 3 |
| It showed the summary of experiment design of dataset of GSE29848 used in our study. In Chalamalasetty et al.’s study, Msgn1 was induced with doxycycline (PlusDox) and uninduced cells (MinDox) were used as controls. Samples were collected at three different time points including 12h, 24h and 48h. Experiments were performed in triplicate. |
Notch signaling pathway is down-regulated in 12h and 24h, while it is upregulated in 48h. Wnt signaling pathway is down-regulated in 24h and 48h (shown in Table 2). It has been reported that chondrogenesis could be inhibited by Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway would be down-regulated during chondrogenesis under the induction of TGF-β [22[. We presume that Notch signaling pathway may play a vital role in the later stage of somitogenesis. While in the middle and later periods, Wnt signaling pathway may reduce its effects on somitogenesis.
Table 2. The signaling pathways significantly down or up-regulated in 12h, 24h and 48h during somitogenesis
| Signaling pathway | Functional class | 12h | 24h | 48h |
| p53 signaling pathway | Cell growth and death | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ |
| GnRH signaling pathway | Endocrine system | | ↓ | ↓ |
| Adipocytokine signaling pathway | Endocrine system | | ↓ | ↓ |
| PPAR signaling pathway | Endocrine system | | ↑ | |
| Insulin signaling pathway | Endocrine system | | ↓ | |
| Chemokine signaling pathway | Immune system | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ |
| RIG-I-like receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ |
| Toll-like receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | ↑ | | ↓ |
| NOD-like receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | ↑ | | ↑ |
| Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway | Immune system | ↑ | | |
| B cell receptor signaling pathway | Immune system | | | ↓ |
| Neurotrophin signaling pathway | Nervous system | ↑ | ↓ | |
| VEGF signaling pathway | Signal transduction | ↑ | | ↓ |
| Calcium signaling pathway | Signal transduction | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| Notch signaling pathway | Signal transduction | ↓ | ↓ | ↑ |
| Hedgehog signaling pathway | Signal transduction | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| ErbB signaling pathway | Signal transduction | ↑ | ↓ | |
| MAPK signaling pathway | Signal transduction | ↑ | ↓ | ↓ |
| mTOR signaling pathway | Signal transduction | | ↓ | ↓ |
| Wnt signaling pathway | Signal transduction | | ↓ | ↓ |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway | Signal transduction | | ↓ | ↓ |
| Jak-STAT signaling pathway | Signal transduction | | | ↓ |
| Here, all of the signaling pathways at 12h, 24h and 48h during somitogenesis were shown. We compared the signaling pathways with KEGG pathway maps, and obtained the functional classification of these signaling pathways presented in second column. Finally, we performed the down or up-regulated information of each signaling pathways at each time points. |
Network construction and dynamic regulation during somitogenesis
The signaling pathways network was reconstructed to reveal the dynamic regulation during somitogenesis at three different time points including12h, 24h and 48h (shown in Figure 3). MAPK and Hedgehog signaling pathways can activate Notch signaling pathway by activating Akt2 and Gli2 respectively [23, 24[. Inhibition of the MAPK signaling pathway decreases the expression of Notch1 and Hes1. Notch1 and Hes1 are downstream effectors of Notch signaling pathway and Hes1 is the target gene of Notch1 [25,26]. Hes7, a segmentation clock, can inhibit Notch target genes, so we hypothesize that Hes1 may have the similar effect. Besides, the relationship of genes and pathways specially involved in 24h and 48h was showed in Figure 2. TGF-β signaling pathway activated Wnt signaling pathway via the expression of TGF-β1 [22,27]. Wnt1 is target gene of Wnt signaling pathway and Wnt1 can induce the activation of mTOR signaling pathway [28]. Members of the Transforming Growth Factor-beta (TGFβ) superfamily of cytokines play crucial roles in pluripotency and differentiation of embryonic stem cells in vitro, which are essential for early mammalian embryonic development [29[. mTOR signaling pathway can influence muscle development in mice by majoring the accumulation of protein level in somites [30].
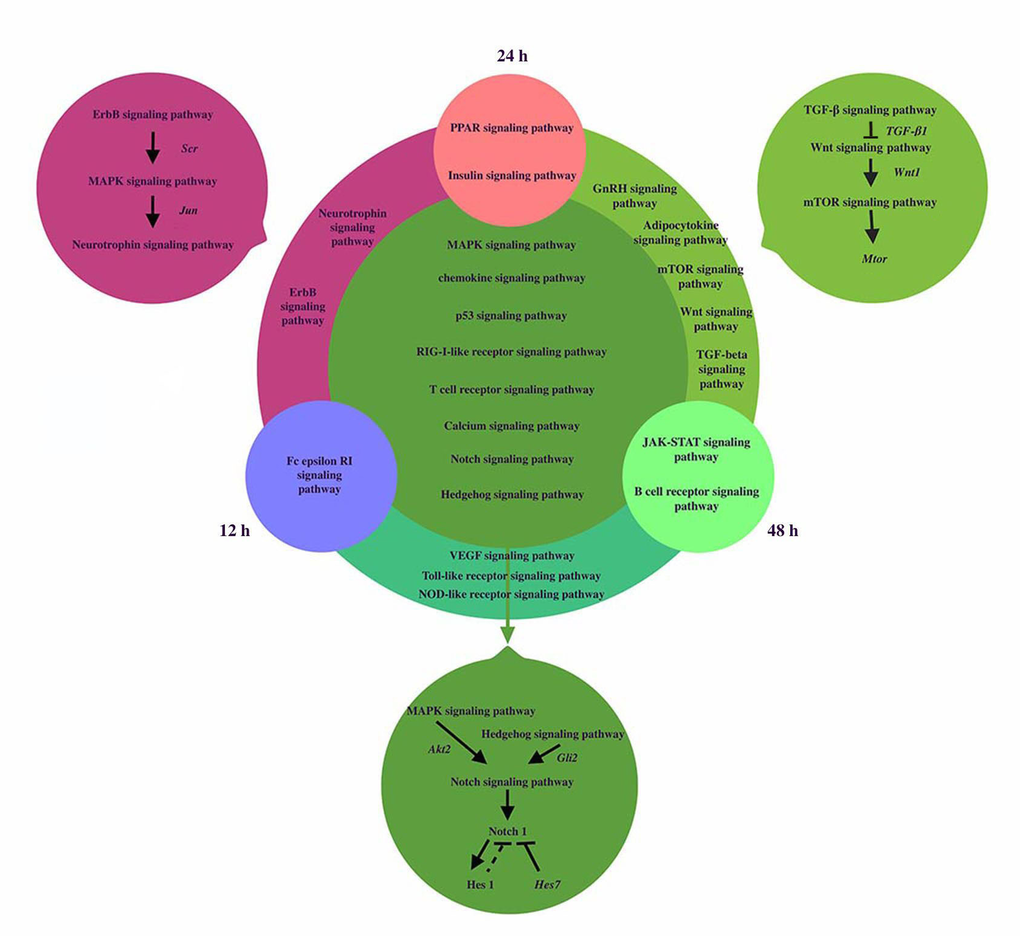
Figure 3. The coexpression networks of related pathways during somitogenesis. We analyzed the signaling pathways network of dynamic regulation during somitogenesis at three different time points including12h, 24h and 48h. Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway was only significantly regulated in 12h, PPAR signaling pathway and Insulin signaling pathway were significantly regulated in 24h, Jak-STAT signaling pathway and B cell receptor signaling pathway were significantly regulated in 48h. 2 signaling pathways played roles at both 12h and 24h. Erb signaling pathway can activate Neurotrophin signaling pathway via MAPK signaling pathway. Jun, regulated by MAPK signaling pathway, induce neurotrophin activation. 5 signaling pathways regulated significantly at 24h and 48h, TGF-β signaling pathway activated Wnt signaling pathway via the expression of TGF-β1. Wnt1 is target gene of Wnt signaling pathway and Wnt1 can induced the activation of mTOR signaling pathway. 3 signaling pathways regulated significantly at 12h and 48h. 9 signaling pathways regulated at three different time points. MAPK and Hedgehog signaling pathways can activate Notch signaling pathway by activating Akt2 and Gli2 respectively. Notch1 and Hes1 are the downstream effectors of Notch signaling pathway and Hes1 is the target gene of Notch1. Hes7 can inhibit Notch target genes, so we hypothesize that Hes1 may have the similar effect. For simplicity, several target genes, gene products, and regulatory interactions are not shown.
Erb signaling pathway can activate Neurotrophin signaling pathway via MAPK signaling pathway. The ErbB signaling pathway regulates proliferation, differentiation, cell motility, and survival. MAPK pathway is a downstream target of ErbB receptors. The highly conserved module of MAPK cascade participates in a variety of cellular functions, including cell proliferation, differentiation and migration. Neurotrophins belong to the category of trophic factors, which are involved in the differentiation, growth and survival of cells [31]. Several intracellular signaling pathways including the MAPK cascade would be stimulated by the activation of multiple ligands such as the epidermal growth factor (EGF) on ErbB receptor, which is regulated by Src [32]. From Jun Yamauchi et al.’s study, Jun, regulated by MAPK signaling pathway, induces neurotrophin activation [33]. All the genes mentioned above can be found in Tables 4, and they confirm our analysis once again.
Log2 ratios of the normalized expression levels of Hes1,Notch1,Tgfβ1,Wnt1,Akt2 and Dli2 are presented (shown in Figure 4). Error bars demonstrate standard deviation of 3 biological replicates. The expression of Hes1and Tgfβ1 was upregulated under Msgn1 overexpression over a 48-hour time course. The expression of Notch1 was variable, presumably reflecting the dynamic expression of a cyclic gene, but was generally elevated by Msgn1 overexpression. Tgfβ1 expression was upregulated in treated groups compared with untreated ones at 24h, while Wnt1 expression was just opposite, which confirms Tgfβ signaling pathway can activate Wnt signaling pathway via the expression of TGF-β1. The expressions of Notch1 and Hes1 were upregulated in treated groups compared with untreated ones from 12h to 48h, which was consistent with results shown in Figure 4. The expressions of Akt2 and Gli2 were downregulated compared with the control group while the Notch1 expression was upregulated in treated groups, presumably reflecting other signaling pathways. The Wnt signaling pathway, for example, activates the Notch signaling pathway.
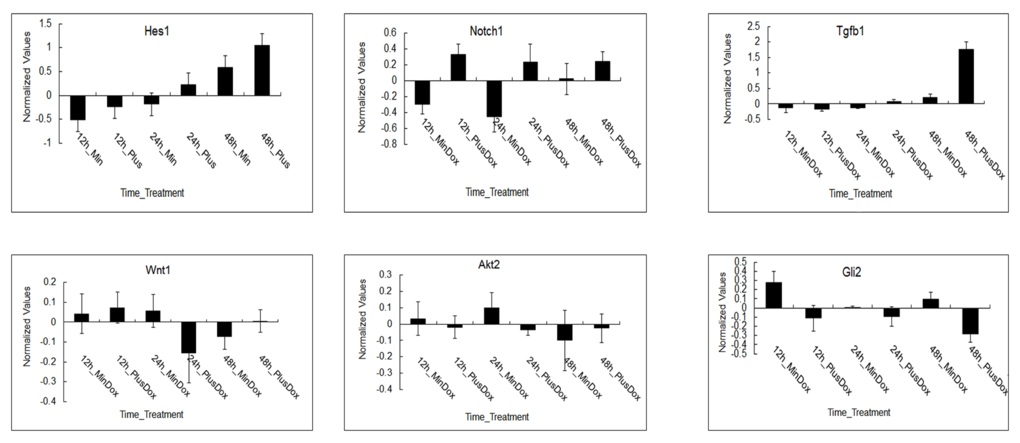
Figure 4. The expression patterns of regulated genes in major signaling pathways during somitogenesis under Msgn1 overexpression. Microarray analysis of of gene expression in the absence and presence of Dox over a 48 hour timecourse. log2 ratios of the normalized expression levels of Hes1, Notch1, Tgfβ1, Wnt1, Akt2 and Dli2 are presented. The expression of Hes1 and Tgfβ1 was upregulated under Msgn1 overexpression over a 48 hour timecourse. Notch1 expression was variable, presumably reflecting the dynamic expression of a cyclic gene, but was generally elevated by Msgn1 overexpression. Tgfβ1 expression was upregulated in treated groups compared with untreated ones at 24h, while Wnt1 expression was just opposite. It may confirm that TGF-β signaling pathway could activate Wnt signaling pathway via the expression of Tgfβ1. Notch1 and Hes1 expressions were both upregulated in the treated groups compared with untreated ones from 12h to 48h. The expression of Akt2 and Dli2 were both downregulated compared with control group while Notch1 expression was upregulated in treated groups, presumably reflecting other signaling pathways, Wnt signaling pathway for example, activate Notch signaling pathway. Here error bars indicate standard deviation of 3 biological replicates.
To further examine whether Msgn1 could regulate these genes expressions during mESC differentiation, we generated a flag-tagged Msgn1-overexpressing mESC line using a PiggyBac vector (PB-Msgn1) in which Msgn1 expression was efficiently enhanced (Figure 5A). According to our quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR) results, the expression levels of above six genes at day 2 EBs could be detected. As shown in Figure 5B, the overexpression of Msgn1 was able to induce higher expression levels of Hes1, Notch1 and Tgfβ1 than the PB empty vector, while inhibiting the expressions of Wnt1, Akt2 and Gli2. The validation of our qRT-PCR results was consistent with the previous gene expression profiles.
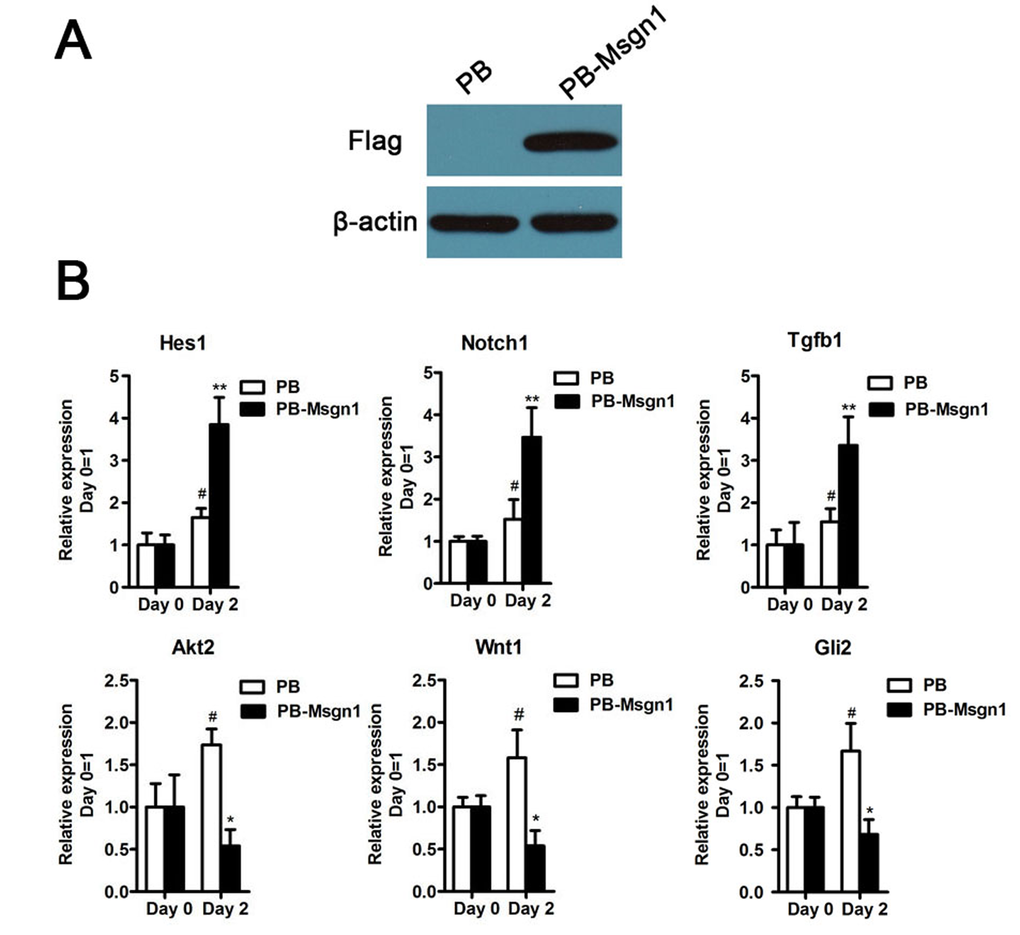
Figure 5. The validation results of qRT-PCR. (A) Flag-tagged Msgn1 was introduced into 46C mESCs and the protein level of Flag-tagged Msgn1 was determined by Western blot. β-actin was used as a loading control. (B) qRT-PCR analysis of the indicated gene expression for the indicated time in mESCs and mESCs-derived EBs. Data represent mean±s.d. of three biological replicates. #p < 0.05 vs PB:Day 0. *p < 0.05, **p<0.01 vs PB-Mgsn1:Day 0.