Introduction
The degree to which individuals respond to cancer therapy is highly varied among each cancer patient, reinforcing the belief that each case is heterogeneous and unique. Despite this, research aims to identify common themes and mechanisms of cancer development that could be widely adopted to predict, detect, and target the disease to improve patient outcomes. While an immense variety of cellular malfunctions exist that lead to cancer, there are key, widely accepted, commonalities that serve as hallmarks of cancer [1]. These hallmarks include selective growth and proliferative advantages, altered stress responses, metabolic rewiring, modified vascularization and the ability to invade and metastasize. Cancer cells can also exhibit enhanced genomic instability, a result of multiple mechanisms, including dysregulated DNA synthesis and ineffective mitotic checkpoints [2, 3]. Normally, cells with DNA double strand breaks above a given threshold, generally believed to be determined by p53 [4], would be diverted down the programmed cell death pathway and prevented from replicating [5, 6]. Cancer cells notoriously bypass the usual quality control checkpoints and continue to replicate despite multiple mutations. This persistent damage can then cause a positive feedback loop with promiscuous replication of DNA harbouring damage resulting in further dysregulation of protein function and expression, generating yet greater deregulated cell cycle progression. The ability to continually replicate regardless of excess damage also implies that there is a suppression of apoptotic pathways, which would normally terminate a normal cell undergoing this malignant transformation [7]. While the specific genes altered may differ between malignancies, the defects may produce similar effects, as multiple genes regulate similar pathways.
The Anaphase Promoting Complex (APC) and cancer development and progression
Oncogenic-like changes (deregulated apoptosis, inadequate quality control of the cell cycle, and accumulated DNA damage) can be influenced by competing stress responsive and nutrient sensing pathways. In the Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe yeast eukaryotic model systems, a wealth of literature links the antagonistic interactions between the stress and nutrient sensing pathways as critical for genome stability and longevity [8–14]. The Anaphase Promoting Complex (APC) appears to be at a critical nexus point that regulates the molecular equilibrium of these pathways [15–23]. The APC has been observed in yeast to interact with stress response pathways to mediate the response to multiple stresses, with mutations to the APC resulting in genomic instability leading to a variety of phenotypes [15, 16, 18–20, 23, 24]. Indeed, studies using human cell culture show that the APC, when bound by the CDH1 coactivator subunit (APCCDH1), controls cell cycle arrest in response to stress [25, 26]. It was observed that APCCDH1 inactivation represents the commitment towards cell cycle re-entry. Active APCCDH1 facilitates entrance into a quiescent state when stress is encountered, but not when APCCDH1 is inactivated. Thus, this provides an explanation for why impaired APCCDH1 activity is associated with enhanced genomic instability and cancer progression [27–31], as cell cycle arrest is blocked in the presence of DNA damage, allowing mutations to accumulate.
The APC is a large, structurally and functionally conserved ubiquitin ligase that targets inhibitors of mitotic progression and interphase arrest for ubiquitin- and proteasome-dependent degradation. In humans, the APC is a 1.5 megadalton complex composed of 19 subunits, 15 of which are unique [32]. The yeast complex is equally large with 13 unique subunits, lacking only the human APC7 and APC16. The conserved APC is composed of 3 structural motifs: the platform, the TPR lobe and the catalytic core. The TPR lobe contains many of the subunits targeted for post-translational modifications, while the catalytic core contains APC11, APC2 and APC10 that transfer the ubiquitin molecule from the E2 to the substrate molecule. The platform (APC1, APC4 and APC5) connects the TPR lobe and the catalytic core. The APC, as discussed in this review, interacts with a great number of proteins for proper regulatory control and function. It is also targeted by a variety of signalling networks that phosphorylate, ubiquitinate and acetylate APC subunits, mostly within the TPR lobe, but also APC1. The large structure and intricate assembly is likely required to sort through the many unique, but intertwined signalling mechanisms that control APC activity. APC activity is primarily controlled through exclusive binding by one of 2 activator subunits, CDC20 or CDH1, to form the APCCD20 and APCCDH1 complexes, respectively; CDC20 promotes anaphase and mitotic progression, while CDH1 regulates mitotic exit and G1 progression [33, 34]. It has been observed that the APC activator and eventual substrate, CDC20, accumulates in many types of cancer cells in vitro and in vivo [35–38]. This suggests that CDC20-dependent activation of the APC may be a critical component of cancer development and behavior. This is further supported by the observation that expression of both APC2 and APC7 are elevated in acute myeloid leukemia cell lines and patients [39], and that overexpression of APC11 mRNA and protein has been reported in lung cancer cells and patients [40]. Indeed, silencing of CDC20 using RNA interference in pancreatic cells lines augmented cytotoxicity when exposed to chemotherapies [41]. Furthermore, use of the pharmacological agents APCIN or pro-TAME, which inhibit the binding of CDC20 to the APC (and thus APCCDC20 formation) resulted in increased apoptosis and death in multiple cancer cell lines, indicating that inhibition of the APC may be a useful anticancer approach [42–44]. Moreover, an interesting recent study showed that cancer cells displaying chromosome cohesion defects were synthetically lethal with APC subunit depletion, providing further evidence that APC inhibition may be a powerful means to killing cancer cells [45]. As well, direct inhibition of the APC by peptides elevated sensitivity of cancer cells to microtubule poisons [46].
Opposing the idea that APC activity is an important driver of cancer development and that inhibiting its activity is a useful approach to treating cancer, are the multiple observations that many APC substrates are elevated in various unrelated cancers, both at their mRNA and protein levels. Many of these substrates are also notable for being markers for poor prognosis [23, 47–51]. The accumulation of these substrates indicates two potential mechanisms; either the accumulation of these proteins leads to APC-independent cancer progression, or it is impaired APC function that leads to the accumulation of multiple substrates and cancer progression. The accumulation of APC targeted mitotic kinases like PLK1, MPS1, and Aurora A/B in cancer has led to efforts to target these molecules for anticancer therapy [52]. However, regardless of in vitro successes, lead molecules targeting APC substrates have had limited success in the clinic [53–55]. Nonetheless, while monotherapy may have limited success, these studies reveal that combinatorial treatment with other anticancer drugs shows promise in clinical trials. Thus, the accumulation of multiple APC-targeted proteins in a single cancer cell may be due to a failure of their regulated degradation, suggesting that generalized APC E3 activity may in fact be impaired in cancer cells. Observations that mutations to several APC subunits are associated with cancer progression [56, 57] supports the notion that APC activity may in some cases ward off cancer progression. In addition, the development of small molecule inhibitors of the Spindle Assembly Checkpoint (SAC; inhibits APC activity), TTK/MPS1 protein kinase inhibitor (TTKi) and Mad2 Inhibitor 1 (M2I-1), are observed to be potent anticancer agents in vitro [31, 58–62]. In general, the SAC inhibits the APC by sequestering away CDC20 until cells are ready to enter mitosis [63]. SAC inhibitors lead to enhanced APC activity and a shortened mitosis, suggesting that APC activity may be critical for TTKi and M2I-1 anti-cancer function. This was validated by a report showing that cells treated with siRNA against APC subunits APC4 or APC13/SWM1 developed resistance to the SAC inhibitor [31]. This opens the possibility that activation of the APC may enhance cancer treatment by potentially bypassing the spindle assembly checkpoint, pushing highly damaged cells inappropriately into anaphase prior to sufficient DNA repair, causing mitotic catastrophe.
Recent work demonstrates that the aberrant accumulation of many mRNAs involved in the regulation of APC function and mitotic progression in cancer cells are tightly linked, suggesting that the APC plays a general role in protecting against cancer development and/or progression. It was observed that the accumulation of CDC20 in tissues from a variety of unrelated malignancies was associated with a cluster of 139 genes that were likewise also markedly overexpressed. Many of the genes in the CDC20-associated gene signature defined genes involved in cell proliferation, DNA damage response, and chromosome segregation [37]. This CDC20-associated gene set was originally found overexpressed in glioma transcriptomes, and was found to be a robust predictor of poor clinical prognosis in over 1,000 patient datasets investigated. This adds further support for the notion that APC function may be a critical trigger for the development and progression of multiple cancers.
APC function
The APC is most often considered in terms of its mitotic functions. However, there are many ancillary functions that are performed by the APC including: maintaining genomic stability [19, 64–66], regulating interphase progression [67–69] and apoptosis [70, 71]. Dysregulation of these additional functions can be found in cancer. Both of the APC coactivators have tumor related functions; CDC20 is a well-known oncogene which drives improper cell proliferation [36, 49, 72–74], while CDH1 is considered a tumor suppressor that regulates mitotic exit, entrance to S phase, induces quiescence under stress conditions and maintains genomic stability [16, 66, 75, 76]. We performed a BioGRID analysis of CDC27 to begin to understand the network differences between CDC20 and CDH1, as CDC27 is the key entry point for the coactivators; CDC27 recruits both CDC20 and CDH1 into the APC [77, 78] (Figure 1). BioGRID is a biological database detailing protein-protein, genetic and chemical interactions, as well as post-translational modifications (https://thebiogrid.org). This analysis revealed 144 unique nodes for CDC27, with 602 physical edges, 16 genetic edges and 18 combined physical/genetic edges. Each node, which defines a different gene, was searched on PubMed for interactions with the APC, with APC substrates identified that were uniquely targeted for degradation by CDC20 and/or CDH1. CDC27 was also found to interact with clusters of signalling and trafficking molecules, stress response and DNA repair proteins, CDH1/CDC20 regulators, SAC components, and proteins involved in DNA and RNA processes. This variety of interactors validates the many roles the APC has been described to fulfill.
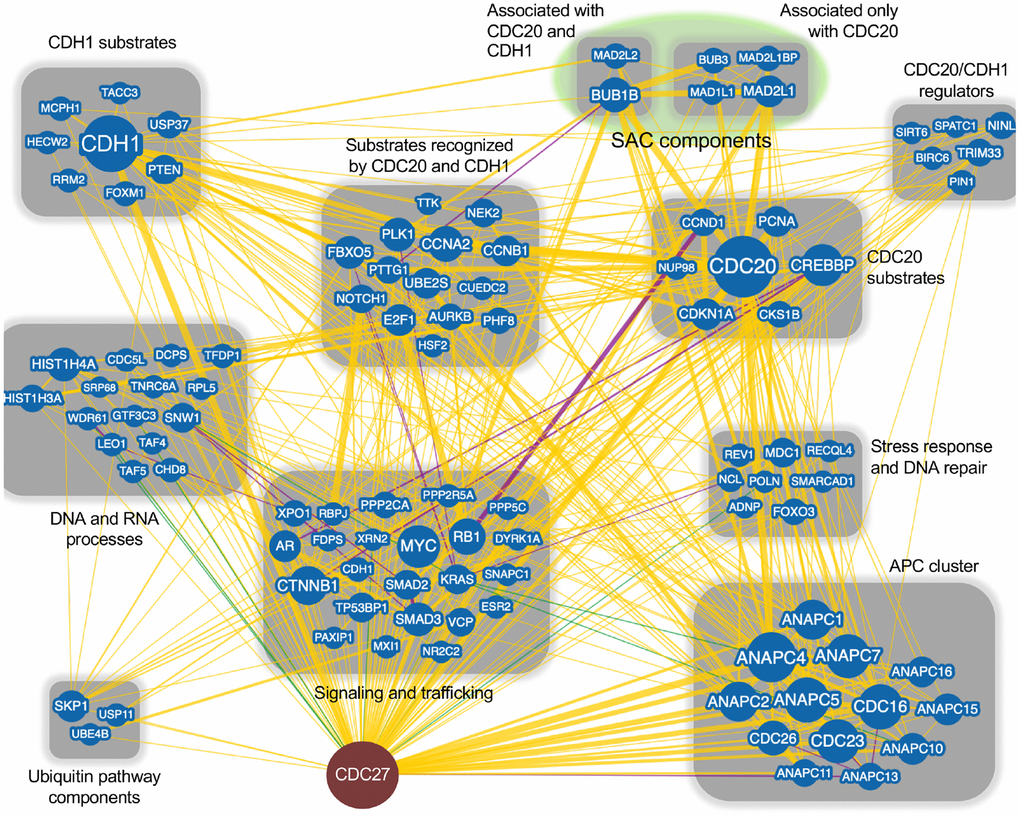
Figure 1. CDC27 network interactors. The BioGRID database was searched for CDC27 interactors. The search resulted in 144 protein nodes (blue circles) that interact with CDC27, producing 602 physical edges (yellow lines), 16 genetic edges (green lines) and 18 physical/genetic edges (purple lines). An edge is the line connecting 2 proteins. Many proteins have multiple interactors, generating multiple edges for a single protein. The search was done with the minimum evidence filter set at 1 (see Supplementary Figure 1 for raw data). Proteins that only interacted with CDC27 (1 edge) were lost when the filter was set at 2 and were not included in this analysis. Each node was manually manipulated for this clustering exercise.
Subsequent BioGRID searches were performed for CDC20 and CDH1 separately to specifically identify common and unique interactors for the 2 coactivators. One hundred and eighty one and 175 interaction nodes were identified for CDH1 and CDC20, respectively, resulting in 819 edges for CDH1, and 919 edges for CDC20. Nodes define proteins interacting with CDC20 or CDH1, while an edge is a line that connects any 2 proteins. A protein node may have more that 1 edge, resulting in more edges than nodes. Thirteen APC subunits were identified by both the CDC20 and the CDH1 searches. Each protein node was searched on PubMed to identify overlaps with APC function. Any protein that did not overlap with the APC on PubMed was not followed further. Physical interactions identified by BioGRID can be part of global screens where individual hits are not discussed in manuscripts, so are not picked up in PubMed searches. So, while these proteins likely physically associate with CDC20 and/or CDH1, not enough information is available to discern the mechanism of association. Further, many proteins may not be direct interactors, but interact through intermediaries defined by complexes. For this analysis we focused on proteins involved in APC inhibition (Figure 2), APC activation (Figure 3) or are potential APC substrates (Figure 4).
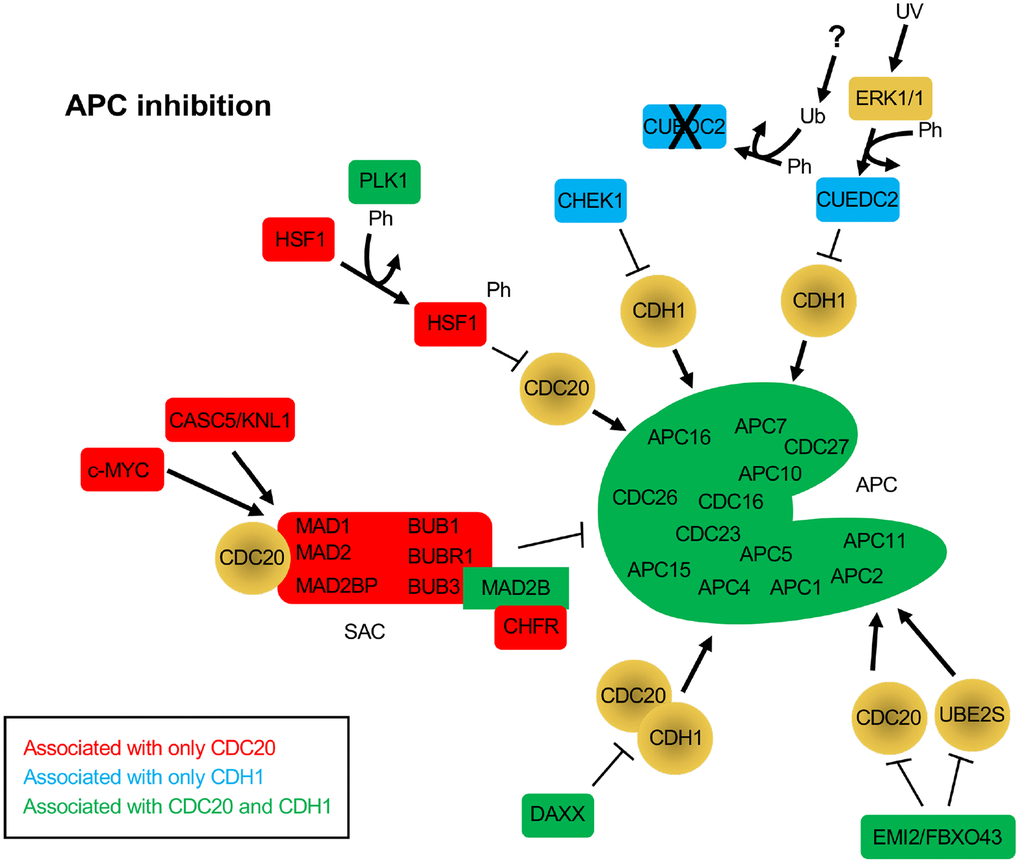
Figure 2. Protein inhibitors of the APC that function through CDC20 and/or CDH1. The BioGRID database was separately searched for CDC20 and CDH1 interactors. To avoid confusion with the cadherin 1 gene (also called CDH1), the alias FZR1 was used to search for the CDH1 coactivator. 181 nodes were identified for FZR1, identifying 801 physical, and 18 genetic edges (see Supplementary Figure 2). For CDC20, 175 nodes were identified, with 911 physical edges and 8 genetic edges (see Supplementary Figure 3). All protein nodes identified were searched using PubMed. Proteins found to inhibit the APC, but not serve as substrates, are shown here. Proteins unique to CDC20 are shown in red, those unique to CDH1 are shown in blue, and those identified in both searches are shown in green. All APC subunits were identified in both searches. Ph, phosphorylation; Ub, ubiquitination.
APC inhibition
A number of proteins were identified that interacted with either or both CDC20 and CDH1 that were not observed as substrates, but were involved in APC inhibition. The SAC components MAD1, MAD2, MAD2BP, BUB1, BUBR1 and BUB3 were all identified only in the CDC20 search, while MAD2B was identified in both searches. As discussed above, the SAC blocks CDC20 from interacting with and activating the APC [63]. Three different proteins were specifically identified in the CDC20 search that work with the SAC to suppress APC activity, c-MYC, CASC5/KNL1 and CHFR (Figure 2). c-MYC was shown to drive the expression of MAD2 and BUBR1, which corresponded to chromosome instability and DNA strand breaks as a result of impaired repair of replication-stress induced DNA lesions in G2 [79]. In addition, the protein CDR1, an APCCDH1 substrate, binds c-MYC to activate its transactivation; elevated accumulation of CDR1 in cancer cells as a result of APC inhibition or defect promotes c-MYC oncogenic function [80]. The protein encoded by CASC5/KLN associates with the SAC to provide a scaffold for protein complex assembly. KNL is phosphorylated by MPS1, a SAC checkpoint kinase that is also an APC substrate, which enables KNL to recruit BUB1-BUB3-BUBR1 to unattached kinetochores and inhibit APC activity [81]. The CHFR protein, described as a tumor suppressor, also promotes the SAC and APC inhibition by facilitating the MAD2-CDC20 interaction [82].
Several other proteins were identified in the CDC20 and CDH1 searches that function as APC inhibitors (CHEK1, CUEDC2, HSF1, DAXX, EMI1/FBXO5 and EMI2/FBXO43). CHEK1 depletion results in disruption of CDC20 and MAD2 localization to kinetochores and decreased CDC20 and MAD2 protein levels [83]. This suggests that CHEK1 is required for APC inhibition. A second study describes this further as it shows that CHEK1 inactivates APCCDH1 in the presence of replication stress by targeting CDH1 for degradation, thereby inhibiting APC activity [84]. CUEDC2 is an interesting protein that functions to inhibit APCCDH1, yet activate APCCDC20. In G1, CUEDC2 binds to and inhibits APCCDH1, thereby stabilizing Cyclin A and promoting G1-S transition [85]. This is blocked by UV irradiation. In the presence of UV, ERK1/2 phosphorylates CUEDC2, leading to ubiquitin and proteasome dependent degradation. The E3 responsible for CUEDC2 degradation has not yet been identified. Activation of APCCDC20 by CUEDC2 is discussed below. HSF1 functions in cancer by inhibiting the interaction of CDC20 with CDC27 and blocking APC activation [86]. The overproduction of HSF1 resulted in the accumulation of APC substrates, inhibited mitotic exit and generated aneuploidy. It was also found that HSF1 phosphorylation by PLK1 was required to bind CDC20 and inhibit APC activity [86]. There are 2 additional APC inhibitors called Early Mitotic Inhibitors (EMI) 1 and 2. EMI1 acts as both an inhibitor and an APCCDH1substrate [25, 26]. EMI1 levels are kept low during G1 by APCCDH1, and then high during S and G2 when APC activity is low. APC inactivation is triggered by CDK2/Cyclin E activity during G1, which coincides with increased EMI1 mRNA expression, which serves to maintain APC inhibition. EMI2, on the other hand, works by inhibiting the interaction of the APC with its E2 component UBE2S in unfertilized Xenopus eggs, thereby blocking unfertilized eggs in metaphase of meiosis II [87]. Upon fertilization, EMI2 is targeted for degradation by the SCFβ-TrCP complex. EMI2 also blocks APC activity by blocking the association of CDC20 with the APC [88]. Lastly, the DAXX protein is often observed to be overexpressed in prostate cancer cells. DAXX encodes APC recognition motifs called destruction boxes. DAXX interacts with both CDC20 and CDH1 via these motifs but does not appear to be a substrate [89]. This interaction is sufficient to disrupt APC function.
APC activation
The CDC20 and CDH1 BioGRID searches also revealed proteins that have not yet been identified as substrates, but have APC activation potential. When SAC activity is no longer required, the complex of MAD2, BUBR1 and BUB3 bound to CDC20 must be disassembled. This process requires ATP, and a number of ATP-dependent activities have been described to assist in the dissolution of the SAC, such as TRIP13, p31comet and the CCT chaperonin [90]. p31comet was not identified in the BioGRID searches, but peptides derived from p31comet have been developed in yeast that bind to the APC and disrupt interaction of CDC20 and CDH1 with the APC [46]. Both TRIP13, and 8 components of the CCT chaperonin (CCT2, CCT3, CCT4, CCT5, CCT6A, CCT7, CCT8 and TCP1) were specifically identified only in the CDC20 search (Figure 3). The CCT chaperonin binds CDC20 and is a necessary factor promoting CDC20 binding to the APC [91]. It was observed that the combined action of the CCT chaperonin with TRIP13 is sufficient to completely disassemble the SAC [90]. TRIP13 has been found to interact with p31comet to induce checkpoint silencing and localizes to kinetochores [92]. Overexpression of TRIP13 is observed in cancers with poor prognosis and is associated with chromosome instability believed to be due to premature checkpoint silencing.
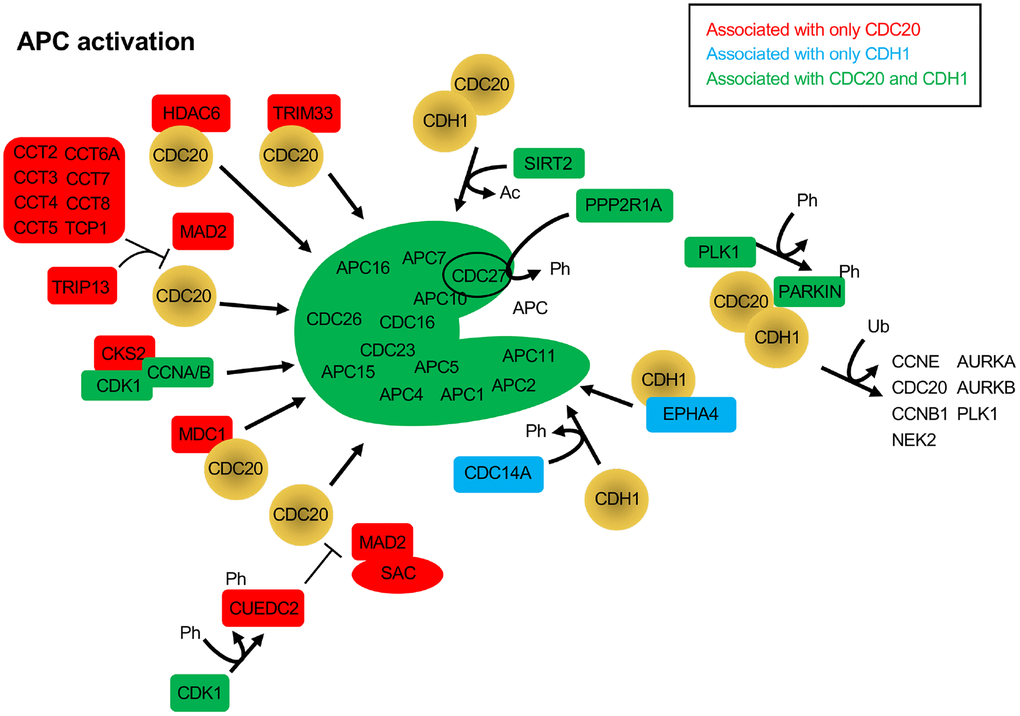
Figure 3. Protein activators of the APC that function through CDC20 and/or CDH1. The BioGRID database was searched for CDC20 and CDH1 interactors. All protein nodes identified were searched using PubMed. Proteins found to activate the APC, but not serve as substrates, are shown here. Proteins unique to CDC20 are shown in red, those unique to CDH1 are shown in blue, and those identified in both searches are shown in green. PARKIN, when phosphorylated by PLK1, is believed to recruit CDC20 and CDH1 to ubiquitinate APC substrates. Ph, phosphorylation; Ac, acetylation; Ub, ubiquitination.
A number of additional APC activators were specifically identified in the CDC20 search: CKS2, CUEDC2, HDAC6, MDC1 and TRIM33 (Figure 3). CKS2 is a Cell division cycle Kinase Subunit that binds to the CDK1/Cyclin A/B complexes to promote their cell cycle driving function. CKS2 is required for meiosis in mammalian cells and mice lacking CKS2 show reduced meiotic development and defective APCCDC20 function [93]. As written above, CUEDC2 inhibits APCCDH1, but can also activate APCCDC20. During mitosis CUEDC2 is phosphorylated by CDK1 [94]. This allowed phosphorylated CUEDC2 to bind to CDC20, and facilitate its release from the SAC component MAD2, thus activating APCCDC20. In another study, APCCDC20 was found to be important for neural development by playing a role in post-mitotic dendrite morphogenesis [95]. This unique APCCDC20 activity was facilitated by HDAC6, a histone deacetylase that is localized to centrosomes, along with CDC20 in neurons. HDAC6 was required for the polyubiquitination of CDC20, and the activation of APCCDC20, driving the differentiation of dendrites. MDC1 is a mediator of a DNA damage checkpoint, and was shown to interact specifically with CDC27 [96]. This interaction required phosphorylated CDC27 and was driven by DNA damage. A subsequent study showed that loss of MDC1 resulted in a mitotic arrest that was BUBR1 and ATM signalling independent [97]. Cells lacking MDC1 had impaired APC activity, reduced CDC20 levels, and failure of remnant CDC20 to bind the APC. TRIM33 is a member of the RING (really interesting new gene) domain E3 ligases, and has been described as a transcriptional corepressor involved in SMAD4 signaling [98, 99]. TRIM33 has also been shown to interact specifically with APCCDC20 and is a component of the mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC), a complex of MAD1, MAD2, BUBR1, BUB3 and CDC20 [100]. The interaction of TRIM33 is complex, as it was shown that TRIM33 will still bind APC in the absence of CDC20, but will not bind APCCDH1. Further, binding assays revealed that TRIM33 only associated with MCC-APC when the SAC was active, not once it was satisfied. This was interpreted to suggest that TRIM33 is required to promote APCCDC20 function once the SAC is inactive.
The phosphatase CDC14A and the receptor tyrosine kinase superfamily member EPHA4 both activate the APC through interactions with CDH1. CDH1 is phosphorylated by CDK/Cyclin B complexes, which blocks interaction of CDH1 with the APC. Dephosphorylation of CDH1 by Cdc14 in yeast and CDC14A in mammalian cells relieves the inhibitory pressure and enables APCCDH1 activation [101]. However, CDC14A does not influence APCCDC20 function. The EPHA4 receptor is involved in neural homeostatic plasticity through interactions with APCCDH1 [102]. Elevated synaptic activity triggers the tyrosine phosphorylation of EPHA4, which then interacts with APCCDH1 to target GLUR1 for degradation to reduce synaptic signalling.
Two additional proteins promote mitotic progression by interacting with both CDC20 and CDH1, but in different ways, SIRT2 and PARKIN. SIRT2 is a protein deacetylase and is a member of the Sir2 family of deacetylases. Sir2 was first studied in yeast as a histone deacetylase, and was shown to have a conserved role in promoting longevity in model systems [103, 104]. SIRT2 has been shown to provide anti-tumor potential by deacetylating both CDC20 and CDH1 to promote their recruitment to the APC and cell cycle progression [65]. Loss of SIRT2 in mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) resulted in stabilized APC substrates, centrosome amplification, and aneuploidy, with mice lacking SIRT2 experiencing increased tumor development. PARKIN, on the other hand, is a RING domain E3 family member that is capable of mono- and polyubiquitinating substrates, with neuroprotective and tumor suppressor potential [105]. Interactions with the APC coactivators were revealed in a study where MEFs lacking PARKIN were shown to have mitotic defects and high levels of multiple APC substrates, such as PLK1, Aurora A, Aurora B and Cyclin B1, for example [106]. This work also revealed that PARKIN forms complexes with either CDC20 or CDH1 that were independent of the APC. Interestingly, depletion of both PARKIN and APC11 recapitulated CDC20 depletion, whereas depletion of PARKIN or APC11 only partially impaired Cyclin B1 degradation. Taken together, it is apparent that there are multiple complex mechanisms in play to regulate APC function. Shifts in the equilibrium of this balancing act could have significant impacts on cell health and viability.
APC substrates
The nodes identified in the BioGRID analyses of CDC20 and CDH1 were all searched by PubMed for any relationship to “anaphase promoting complex”. The resulting literature was assessed for any signs that the particular protein was unstable and targeted for degradation by either APCCDC20 or APCCDH1 or both. This search revealed that 69 of the identified proteins were associated with literature related to degradation by the APC (Figure 4; Table 1). Reviews have been written recently that list APC substrates (25 [107], 46 [32], 16 [108], 13 [38]), but the 69 potential substrates identified here, to the best of our knowledge, is the largest cohort of APC substrates assembled. Literature for the proteins identified here as substrates that were not in previous lists are cited in Table 1 [32, 38, 67, 80, 85, 107–142]. Eight proteins were identified only in the CDC20 BioGRID search, 37 identified only in the CDH1 search, and 24 as targeted by both. OTUD7B was identified in both searches and acts as a cell-cycle regulated deubiquitinase that counters APC function [143]. Confirmation for 5 of the proteins, CCND2, CDK1, CDK2, CDK6 and CDKN2B could not be obtained in the literature. The APC targets CCND1, CDK4, CDK5 and CDKN1A/p21 for degradation, CDK1/2/6 all associate with cyclins that are targeted by the APC, and CKDN2B is a CDK4/6 inhibitor that physically interacts with CDK4/6 [38, 118, 120–122, 134–136]. These proteins are likely substrates, but confirmation requires further analyses. As discussed above, APCCDC20 and APCCDH1 are believed to play opposed roles in cancer development, with APCCDC20 thought to play an oncogenic role [35–38], and APCCDH1 playing a tumor suppressive role [47–51, 56–62]. To gain further insight into these observations we searched each protein in the APC substrate list for a role in cancer using PubMed. All 69 of the putative substrates have been described as being involved in cancer progression. Of the 69 proteins identified in cancer searches, 9 were described as tumor suppressors (orange lettering in Figure 4) and 60 as possible tumor promoters (white lettering in Figure 4). This suggests that proper APC activity is responsible for the targeted degradation of 60 proteins found elevated in tumors and 9 found reduced in tumors. If CDC20 is involved in tumor formation, then we expected that the bulk of the tumor suppressors targeted by the APC would rely on CDC20 activity, whereas the tumor promoters should be specifically targeted by CDH1. As shown in Figure 4, 4 of the 8 proteins potentially targeted by only APCCDC20 are described as tumor suppressors in the literature, while 33 of the 37 proteins potentially targeted only by APCCDH1 are described as oncogenes. Of the 24 proteins potentially targeted by both, all but one has been described as elevated in tumor cells. These observations add significant weight to the idea that the APC plays a critical role in cancer development. It is also clear that the APC could potentially be involved in both tumor promotion and tumor suppression, depending on the activity equilibrium between APCCDC20 and APCCDH1.
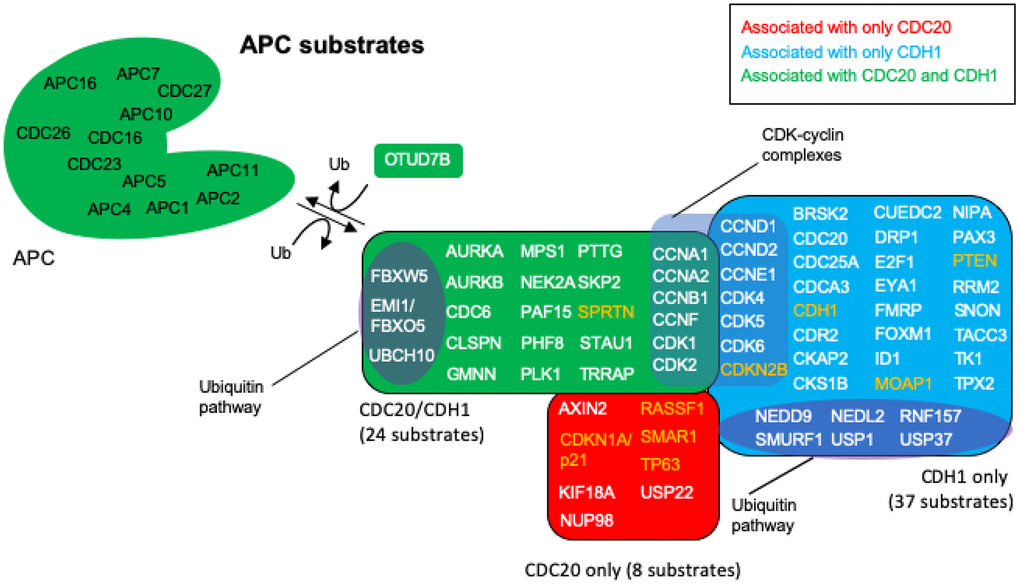
Figure 4. APC substrates that are unique to CDC20 or CDH1, and those that are acted on by both. The BioGRID database was searched for CDC20 and CDH1 interactors. All protein nodes identified were searched using PubMed. Proteins found to serve as APC substrates are shown here. Proteins unique to CDC20 are shown in red, those unique to CDH1 are shown in blue, and those identified in both searches are shown in green. Subgroups within the clusters are highlighted for those involved in the ubiquitin pathway, and those composing CDK-cyclin complexes. Proteins highlighted in white are proteins overexpressed in cancers with oncogenic potential, while those highlighted in orange are mostly downregulated in cancers showing potential tumor suppressing activity. 8 proteins are uniquely targeted for degradation by CDC20 and 37 by CDH1, while 24 protein substrates are shared by both, for a total of 69 potential substrates. The deubiquitinase OTUD7B that deubiquitinates APC substrates was identified in both searches.
Table 1. Human APC substrates identified from BioGRID CDC20/CDH1 queries and PubMed searches of resultant hits.
| CDC20 specific | CDH1 specific | shared by CDC20 and CDH1 |
| AXIN2 [38] | BRSK2 [117] | AURKA [32, 107] |
| CDKN1A/p21 [38] | CCND1 [120] | AURKB [32, 108] |
| KIF18A [109] | CCND2 (?) | CCNA1 [32, 107] |
| NUP98 [110] | CCNE1 [119] | CCNA2 [32] |
| RASSF1 [107, 113] | CDC20 [32, 107] | CCNB1 [32, 107] |
| SMAR1 [114] | CDC25A[32, 107] | CCNF1 [67] |
| TP63 [115] | CDCA3 [32] | CDC6 [32, 107] |
| USP22 [116] | CDH1/FZR1 [32] | CDK1 (?) - interacts with Cyclin B1 [134] |
| CDK4 [118] | CDK2 (?) - interacts with Cyclin E1 [135] |
| CDK5 [121] | CLSPN [136] |
| CDK6 (?) - interacts with Cyclin D1 [32] | EMI1/FBXO5 [25] |
| CDKN2B (?) - interacts with CDK4/6 [122] | FBXW5 [137] |
| CDR2 [80] | GMNN [32, 107] |
| CKAP2 [107] | MPS1/TTK [138] |
| CKS1B [32] | NEK2 [107] |
| CUEDC2 (?) [85] | PAF15 [111] |
| DRP1 [123] | PHF8 [139] |
| E2F1 [107] | PLK1 [32, 107] |
| EYA1 [32] | PTTG [32, 107] |
| FMRP [108] | SKP2 [32] |
| FOXM1 [32, 107] | SPRTN/DVC1 [140] |
| ID1 [32, 108] | STAU1 [141] |
| MOAP1 [124] | TRRAP [142] |
| NEDD9 [125] | |
| NEDL2 [126] | |
| NIPA [127] | |
| PAX3 [128] | |
| PTEN [129] | |
| RNF157 [130] | |
| RRM2 [32] | |
| SMURF1 [131] | |
| SNON [132] | |
| TACC3 [133] | |
| TK1 [32, 107] | |
| TPX2 [32] | |
| USP1 [107, 112] | |
| USP37 [32] | |
Normal activation and activity of the APC E3 Ligase during mitosis
The APC targets specific proteins for ubiquitin- and proteasome-dependent degradation, with as many 69 different proteins serving as targets (see Figure 4). These proteins are found in different tissues at different times, involved in a variety of mechanisms required for mitotic progression and overall cell health, and are defined by specific encoded motifs. The primary motif of proteins targeted by the APC is the destruction box (D-box, RxxLxxI/VxN), which exists on a multitude of APC substrates and is targeted by both APCCDC20 and APCCDH1 [144–146]. Both coactivators contain a WD40 domain that binds APC substrates [146], and assists with APC and E2-ubiquitin interactions to promote APC E3 activity [147–149]. A variety of secondary motifs are recognized by either APCCDH1 or APCCDC20 including the KEN box (KENxxD) [145] and L box (LXEXXXN) [19], which are targeted by APCCDH1, and an LR motif which is targeted by APCCDC20 [109]. These secondary motifs act to target specific proteins [42]. Subunits critical for APC E3 ubiquitin ligase function include APC2 and APC11 which perform the catalytic activity (APC11 encodes the RING domain subunit containing the catalytic cysteine for ubiquitination) [140]. The APC3/CDC27 and APC8/CDC23 subunits bind to the CDC20 and CDH1 coactivator proteins [150, 151], while the APC10 subunit is involved in substrate recruitment within the inner cavity of the APC structure in collaboration with the coactivator subunits [152].
During metaphase, the spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC, composed of MAD1, MAD2, BUBR1, and BUB3) is active, delaying mitotic progression until all sister chromatids are securely attached to the mitotic spindle [153]. The SAC is maintained by the MCC, a multi-subunit complex that inhibits APC activity until all kinetochores are properly secured to a microtubule [109]. The MCC component MAD2, when associated with the kinetochore via MAD1, binds to the N-terminus of CDC20, which then associates with BUBR1 and BUB3 to form the tetrameric MCC. The MAD2-inhibitor, M2I-1, functionally disrupts the MAD2-CDC20 interaction, freeing CDC20 for subsequent APC activation [58]. Recent cryo-EM studies revealed that the MCC complex binds two CDC20 molecules, suggesting that MCC also interacts with CDC20 bound to APC. In the cryo-EM structure, MCC-CDC20 binds to APCCdc20, where MCC-CDC20 occupies the large APCCdc20 central cavity [154–156]. BUBR1 interacts with both CDC20 molecules, thereby disrupting the ability of both CDC20 molecules to bind substrate. This occurs because BUBR1 encodes D-box and KEN-box APC recognition motifs, through which CDC20 binds [157]. Once microtubules are properly attached to the kinetochores associated with chromosomes, the SAC becomes inactivated and CDC20 is released from the SAC so it can in turn activate the APC [158]. There are multiple molecular networks that work together to ensure that the SAC is properly regulated in both positive and negative manners (see Figures 2, 3).
Once the SAC is inactivated, the first of two phases of APC activity relevant to mitosis begins, where the APC promotes anaphase by the ubiquitination (and subsequent proteasomal degradation) of multiple protein targets. Two prominent proteins involved in chromosomal segregation are Securin (encoded by PTTG1, which is targeted by the APC for degradation) and Separase (which is not directly targeted by the APC). Securin is an inhibitory chaperone of Separase, which acts by allosterically altering the conformation of bound Separase to prevent binding to target proteins [159]. Separase is a cysteine protease that cleaves the kleisin subunit of cohesin. Cohesin acts to bind sister chromatids together and cleavage of the kleisin subunit results in dissolution of the cohesin ring binding sister chromosomes together, inducing chromosomal segregation [160, 161]. The APC acts by polyubiquitinating Securin, targeting it for degradation, and enabling Separase activity. The newly activated Separase then triggers chromosomal segregation by cleaving the cohesion kleisin subunit.
While bound to CDC20 the APC will also self-regulate in a negative feedback loop where it targets Cyclin B1 for degradation. At the G2/M transition Cyclin B1 is synthesized to initiate anaphase. Cyclin B1 functions by binding and activating cyclin dependent kinase 1 (CDK1), which phosphorylates multiple targets to drive anaphase, including APC subunits and CDH1 [162, 163]. The Cyclin B1/CDK1 complex is crucial for phosphorylating APC subunits in a manner that promotes APCCDC20 activity while inhibiting interaction of CDH1 with the APC. Thus, the degradation of Cyclin B1 results in the loss of phosphorylation of many targets, including APC subunits, allowing for the replacement of CDC20 by CDH1 [162, 163]. The incorporation of CDH1 into the APC initiates the targeting of a new suite of protein degradation targets and the second phase of APC activity that permits a regulated mitotic exit and maintenance of G1 progression. These targets include, amongst others, CDC20 and FOXM1, and residual Cyclin B1 (Figure 4; Table 1), which a great deal has already been written (for example, see [16, 107, 164]). The role of the APC in regulated mitotic progression and G1 maintenance is essential for the maintenance of chromosomal integrity and genomic stability [76, 165]. Loss of chromosomal integrity drives the heterogeneity of malignant cells and may help promote changes in cancer biology resulting in the acquisition of multiple-drug resistance, metastatic, or other characteristics [166–170].
Dysregulation of CDC20 or CDH1 impacts APC activity and cancer biology
Kaplan-Meier survival plots (https://kmplot.com/analysis/) of patient survival rates when either CDC20 or CDH1 are over- or underexpressed is shown in Figure 5. High level CDC20 expression is associated with poor patient survival rates, whereas high level CDH1 expression is associated with a slightly better survival rate. This is consistent with the literature suggesting that CDC20 and CDH1 interact with a distinct cohort of proteins and pathways (Figures 1–4) and have distinct roles in cell homeostasis when associated with the APC.
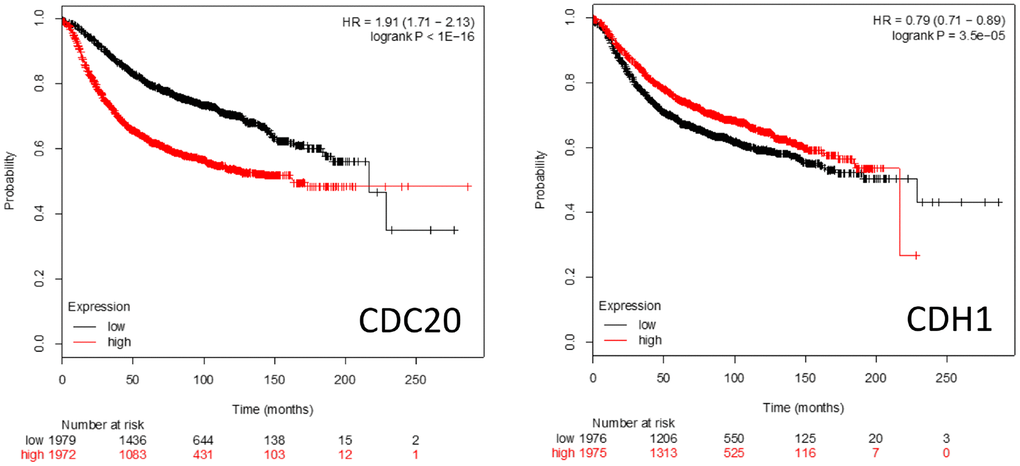
Figure 5. Kaplan-Meier survival plots comparing high vs low expression of the APC coactivators CDC20 and CDH1 mRNAs in breast cancer patients.
CDC20
CDC20 has been identified as being an oncogene [38]. Both overexpression and augmented protein abundance have been correlated with poor prognosis for several unrelated cancer types including brain astrocytoma [72], gastric [171], breast [49], colorectal [172], prostate [36], and pancreatic cancers [74]. A recent study found that patients with overexpression of BUB1B, CDC20, CCNA2 and CDK1 were more likely to exhibit the worst cancers [173]. Increases of CDC20 drive a dysregulated mitotic cycle in part by overwhelming the inhibitory capacity of the SAC; while the SAC is capable of blocking CDC20 function while bound to the APC, it can only simultaneously sequester 2 molecules of CDC20 at a time [154, 158]. Overaccumulation of CDC20 could forcibly activate the APC, despite an active SAC, to drive the cell through an unregulated mitotic cycle (referred to as mitotic slippage) and result in dysregulated proliferation [174, 175]. One obvious mechanism leading to CDC20 accumulation would be the dysfunction of the APC itself, resulting in inefficient CDC20 degradation. However, inhibitory mutations within Speckly-type POZ Protein (SPOP) may also result in CDC20 accumulation, as SPOP promotes the E3 ligase activity of Cullin proteins that contribute to CDC20 polyubiquitination and subsequent degradation [73]. It is thought that by driving improper APC activity (and therefore mitosis) that CDC20 primarily contributes to tumorigenesis. However, the observation that overexpression of CDC20 is accompanied by the overexpression of a host of other genes associated with APC impairment in other cancers [37], including overexpression of other APC substrates (Figure 4), indicates that it may be APC impairment, not specifically CDC20 overexpression, that is important for cancer development and/or progression, in at least some cases.
CDH1
The potential role that CDH1 plays in cell biology and tumor development is different from CDC20, as it appears to act as a tumor suppressor [42]. Loss of CDH1 activity is a common occurrence in cancer development, and the generation of heterozygous CDH1+/- mice that are haploinsufficient incur greater rates of cancer formation [176–178]. This indicates an overall tumor suppressive function. Loss of CDH1 activity generates chromosomal abnormalities [75, 76, 176, 179], elevated sensitivity to DNA damage [180, 181], insufficient loading of Mini-Chromosome Maintenance proteins (MCMs) [75], and premature S phase entry [67, 75, 182, 183]. These abnormalities are a result of loss of key CDH1 functions when underexpressed, which include cell cycle arrest upon nutrient and genotoxic stress [16, 177, 184–186], regulation of S phase entrance [67, 164, 183], and promoting mitotic exit [187, 188]. CDH1 delays S phase progression until the cell is prepared for DNA replication by targeting proteins involved in DNA replication and S phase progression for degradation, such as Cyclin F, SKP2 (subunit of the SCF ubiquitin ligase), ORC1, CDC6 and RRM2 [32, 67]. Three activities have been reported to decrease CDH1 protein levels as cells approach S phase: APCCdh1 autoubiquitination [189, 190], SCFCycF [67] and SCFβTRCP [191]. The complicated relationship between CDH1 and cancer progression was described when suppression of CDH1 in B cell acute leukemia initially resulted in mitotic catastrophe and apoptosis, but long-term CDH1 loss contributed to development of treatment resistance [192]. It was also reported that CDH1 was found overexpressed in many malignant tumor samples, along with other APC substrates [47].
CDH1 accretion may also promote cancer development and progression. CDH1 works antagonistically with the SAC and can act to induce mitotic slippage. [193, 194]. APCCDH1 overactivity from either CDH1 overexpression, or loss of the APCCDH1 inhibitor, early mitotic inhibitor 1 (EMI1), may also result in DNA re-replication through the over-degradation of Geminin [195, 196]. In G2 and S phase, Geminin acts to inhibit CDT1, which is responsible for initiating DNA replication. Therefore, inappropriate loss of CDT1 inhibition may result in DNA replication occurring multiple times, triggering aneuploidy [195–197]. The wide variety of CDH1-associated activities demonstrates its complicated role in cancer progression, and warrants further investigation.
Impact of the overabundance of specific APC substrates on cancer behavior
All APC substrates identified in Figure 4 are individually implicated in tumor development, and many are frequently found to be overexpressed in a variety of cancers (60 of 69 proteins in Figure 4) [47, 49, 198, 199]. These discrete substrates have typically been considered in isolation, rather than as a population of APC substrates as a whole. As detailed below, the combined effect on cell biology with the accumulated overabundances of multiple APC targets includes loss of cell cycle regulation, introduction of promiscuous cycle progression, impaired apoptosis and increased genomic instability. These are classic features of cancer.
Securin
Degradation of Securin is necessary for mitotic progression, and overexpression is a prognostic marker for worsened patient outcomes [49, 198]. Accumulation of Securin can arise from multiple mechanisms. The hPTTG1 gene, encoding Securin, is a downstream target of estrogen receptor (ER) activation, and estrogen receptor positive (ER+) breast related cancers experience elevated Securin synthesis [198]. Securin accumulation may also occur as a result of selected mutations preventing Securin degradation. A specific mutation which results in this phenomenon is a T60A mutation, where threonine 60 (T60) is a crucial phosphorylation site. Substitution of the T60 amino acid prevents a destabilizing phosphorylation event, resulting in delayed, but eventual degradation of Securin [200]. Elevated Securin levels in general, but also resulting from the T60A mutation, result in increased instances of aneuploidy and chromosomal instability, identifying Securin as an important protein requiring tight regulation. Chromosomal defects are achieved by the accumulated Securin protein inhibiting proper chromosomal segregation through Separase inhibition, despite mitotic progression. Securin accumulation also results in elevated instances of cancer metastasis [49, 198].
PLK1
Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) is a serine/threonine kinase that is implicated in tumorigenesis and serves as a prognostic marker for worsened patient outcomes in multiple cancers, including non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) [201], head and neck squamous cell carcinomas [202], and breast cancer [48, 203, 204]. Evolutionarily conserved PLK1 function is important for mitotic progression and exit; PLK1 (Cdc5 in yeast) phosphorylation targets include the APC subunits APC1, APC6, and APC3, and this is important for APC activation [205, 206]. PLK1 also phosphorylates the APC inhibitor EMI1 and inhibits the SAC (reviewed in [207]). Phosphorylation of EMI1 generates a phospho-degron motif that targets EMI1 for SCFβ-TRCP-mediated degradation, thereby alleviating APC inhibition. It was also observed that expression of hyperactive PLK1 bypassed the mitotic block induced by nocodazole, which could be restored if a non-degradable Cyclin B1 was expressed. This suggested that hyperactive PLK1 induces a spindle checkpoint failure and prematurely activates the APC. On the other hand, normal PLK1 activity functions to promote numerous processes including chromosomal segregation, cytokinesis, mitotic entry and centrosome maturation [208–211]. A prevalent phosphorylation event performed by PLK1 is on the Cohesin protein to assist Separase in cleaving the cohesion chromatin complex [160]. Errant PLK1 activity in cancer also results in impaired apoptotic pathways [212] and PLK1 overexpression actively promotes tumor formation after induction of DNA damage [213].
Aurora A and B kinases
The Aurora A and B kinases have different targets, yet both phosphorylate proteins that promote chromatid segregation during cell division [214]. In multiple malignancies including colorectal [199], breast [215], pancreatic [216], and laryngeal [217] gene amplification and subsequent overexpression of Aurora A and B have been detected. Overexpression of either kinase induces chromosomal instability and tumorigenesis [215, 217], while Aurora A specifically has been found capable of overriding the mitotic arrest induced by SAC through its inhibitory phosphorylation of the BUB1 subunit, and causing mitotic slippage [218, 219]. Cancer cells are often observed to undergo mitotic slippage to avoid cell death when treated with mitotic blockers [221]. Furthermore, overexpression of Aurora A results in the aberrant phosphorylation of p73, a tumor suppressor with similarities to p53 [222, 223]. Phosphorylation of p73 by Aurora A inhibits p73 by triggering its nuclear exclusion, thereby preventing p73 from activating normal apoptotic pathways in response to DNA damage. Phosphorylation of p73 also results in further reduction of SAC activity, promoting mitotic slippage. This arises from p73-phospho-dependent dissociation of the MCC-CDC20 complex while cells are undergoing mitosis [224]. Aurora B has the opposing effect with regards to mitotic slippage, where it inhibits mitotic slippage by destabilizing kinetochores of improperly aligned chromosomes [225, 226]. The cumulative effects of the overactivity of Aurora kinases results in resistance to multiple chemotherapeutics including cisplatin and paclitaxel [218, 219, 224].
NEK2A
NIMA related kinase 2A (NEK2A) is a splice family-member of serine/threonine kinases whose normal function is to promote the separation of centrosomes [84]. NEK2A accumulation serves as a prognostic marker for poor patient outcomes, promotes cancer cell proliferation, and is found to be upregulated across a multitude of cancers including prostate, breast, colorectal, cervical, hepatocellular carcinoma, and lung cancer [227]. NEK2A-dependent phosphorylation during mitosis serves to destabilize its targeted proteins, including centrosome linker proteins and microtubule stabilizing proteins [228, 229]. Upregulated NEK2A activity results in centrosomal defects and chromosomal instability, a hallmark molecular marker of cancer development [230, 231]. Increased NEK2A activity can also contribute to chemotherapy resistance, as NEK2A accumulation promotes ABC transporter activity through phosphorylation, as well as correlates with elevated expression of ABC transporters, themselves associated with multiple drug resistance [227].
SNON
SNON (SKI Novel, SKIL) is targeted for degradation by the APCCDH1 during interphase and its overabundance contributes to tumorigenesis, owing to its ability to inhibit transforming growth factor β (TGFβ) pathways [232, 233]. TGFβ signaling pathways impact a wide variety of processes in healthy cells to prevent cell division, induce apoptosis, promote cellular differentiation, and homeostasis. However, errant TGFβ signaling, including both over and under activity, results in cancer development and progression. Overactivity of TGFβ pathways promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, a key mechanism in the development of cancer [234–236]. Meanwhile, underactivity permits cancer progression [236]. Normal SNON activity acts to block TGFβ pathways prior to TGFβ activity via inhibition of SMAD2 and SMAD4, which are activated by TGFβ. After the binding of TGFβ to its targeted receptors and initiating its signaling pathways, SNON is targeted for degradation in a negative feedback loop by newly activated SMAD3 [232, 233]. During tumor progression, the overaccumulation of SNON prevents this negative-feedback from TGFβ, as SMAD3 is unable to sufficiently suppress SNON activity. The net result is that TGFβ signaling pathways remain impaired, permitting cancer progression [232–233]. SNON overexpression also specifically contributes to ER+ breast cancer development as SNON acts to enhance ER signaling pathways. To act in this manner SNON binds ERα-subunits that have translocated to the nucleus and enhances ERα transcriptional activity [237].
FOXM1
The protein Forkhead Box M1 (FOXM1) is a member of the Forkhead Box (FOX) transcription factor family and primarily serves to promote the cell cycle and proliferation [238, 239]. Normal FOXM1 activity advances the cell cycle at the G1/S and G2/M transitions by transcribing genes that encode proteins that inhibit cell cycle blockers. One prominent example of this mechanism is the promotion of transcription of genes encoding the SKP2 and CKS1 proteins, subunits of the SCF E3 ubiquitin ligase [240]. Targets of the SCF include prominent tumor suppressors such as p21Cip and p27Kip that act to inhibit a variety of CDK proteins to prevent cell cycle progression through the G1/S transition [240, 241]. By driving the synthesis of SCF components (SKP2 and CKS1), FOXM1 initiates its own destruction, as 2 different SCF complexes, SCFFBXL2 and SCFFBXO31, target FOXM1 for degradation, with SCFFBXO31 specifically targeting FOXM1 at the G2/M boundary and SCFFBXL2 targeting FOXM1 in gastric cancer cells [242, 243]. Interestingly, FOXM1 also transcribes a number of APC substrates and activators to enter mitosis (such as CDC20, Cyclin B1, Cyclin B2, and CDC25B) [24, 244–248]. Like the SCF, activation of the APC also initiates FOXM1 destruction, as APCCDH1 targets FOXM1 for degradation at mitotic exit [164, 249]. FOXM1 levels are therefore heavily monitored and regulated. Elevated levels of FOXM1 are generally found in normal rapidly dividing cells [239, 240] and because of this, FOXM1 has received significant attention for its role in tumorigenesis; notably, its overexpression serves as an important prognostic marker for poor patient outcomes [250–253]. Errantly elevated FOXM1 activity has been linked to cancer metastasis [254], inhibition of apoptotic pathways [255, 256], and improper cell proliferation [257, 258]. On the hand, loss of FOXM1 resulted in prolonged G2 and delayed entry into mitosis, with an accompanying increase in aneuploid cells composed of chromosomes numbers ranging from 20-160 [246].
CDC6
CDC6 contributes to the regulation of DNA replication as part of the DNA origin recognition complex (ORC) along with CDT1 [184, 259]. CDC6 assists in the loading of MiniChromosome Maintenance proteins 2-7 (MCMs) onto the ORC [260, 261], and is required for DNA replication [262]. CDC6 in human cells is targeted for degradation by the ACPCDH1 complex [263–265], whereas in yeast it appears that Cdc6 degradation requires the SCFCdc4 complex [266, 267]. Even though Cdc6 degradation appears distinct between humans and yeast, its importance in DNA replication remains a commonality. MCM complexes serve as origins of replication for DNA [268], recruiting DNA stability proteins [269], and interact with the DNA repair proteins ATM and ATR to facilitate repair [270]. Impaired MCM activity results in genomic instability and an exacerbated S phase [271]. Aberrant MCM activity also results in inappropriate DNA synthesis and cellular replication [272]. Overexpression of CDC6 is often detected simultaneously with elevated CDT1 and MCM expression in a variety of cancers [273–277]. It has been established that the combined overexpression of CDC6 (both independent of, and in conjunction with, CDT1) and MCM2-7 levels correlate with poor patient prognosis in breast cancer [275]. Opposed to observations made when CDC6 is overexpressed, inappropriate CDC6 depletion subsequently results in centrosome over-duplication and premature chromosomal segregation [278].
Geminin
Geminin plays a multifaceted role in impacting cancer development when overexpressed or overabundant. Its normal functions include binding, stabilization and inhibition of CDT1 to prevent improperly timed DNA synthesis [197, 279, 280]. Proper quantities of Geminin are necessary to protect the genome from re-replication by CDT1 [280]. Geminin is degraded by APCCDH1 during mitosis and G1, but during S and G2 when the APC is inactive, Geminin can begin to accumulate [281, 282]. Upon accumulation, Geminin will bind and inhibit CDT1 [279]. Due to this function, Geminin interacts with and downregulates the CDT1/CDC6 MCM pathways mentioned above. When overexpressed in cancer, Geminin promotes metastasis [274, 283], and results in poorer patient outcomes [284, 285]. It should be noted that while over-abundance of any one of these APC substrate proteins is associated with cancer development/progression, defects to APC function may lead to the over-abundance of the majority of them. This holds the potential for the development of devastating disease states.
Contribution of APC defects to a dysregulated cell cycle
Studies supporting the necessity for the precisely timed cell cycle stages through target degradation by the APC have been carried out, indicating how APC disruptions may lead to cancer [26–32]. The three principle roles of the APC regarding control of the cell cycle include promoting mitotic progression (or inducing mitotic slippage), regulating the entrance to S phase, and inducing cell cycle arrest [16, 67, 183, 185, 193, 286, 287].
Mitotic slippage
Incongruous and/or sustained SAC activation causes mitotic arrest [63, 214]. However, after prolonged arrest some cells can undergo an uncontrolled mitotic progression referred to as mitotic slippage, generating a potential chemotherapy-resistant state in those cells able to pass through this checkpoint inappropriately [220, 221, 288, 289]. There are multiple common consequences to mitotic slippage. First, the cell is likely to proliferate in an unregulated manner [290]. Mitotic slippage can also result in increased chromosomal damage and mis-segregation [291, 292]. Lastly, mitotic slippage induces resistance to chemotherapies disrupting microtubule formation (chemotherapeutics such as Paclitaxel falls under this category). This is due to microtubule poisons relying on prolonging SAC activity in cells that do not carry a heavy load of chromosome instability, but to the point of triggering mitotic slippage, a mechanism dependent on APC driving mitosis despite SAC activity [219, 291, 293]. On the other hand, in cells harboring high loads of chromosomal instability due to excess DNA mutations, induction of mitotic slippage has been proposed as a mechanism to kill these cells. Chemicals that inhibit the SAC, such as TTKi’s [294–296] and M2I-1 [58, 62], have been shown to block CDC20 sequestration by the MCC, leading to activation of the APC and effective cancer cell death. It is proposed that premature activation of the APC pushes cells with high loads of chromosome instability into mitotic division before there is time to repair the damage, causing mitotic catastrophe [31].
Improper regulation of the APC can induce mitotic slippage through multiple mechanisms. First, the overexpression of CDC20, as described above, prevents the SAC from inhibiting APC activity due to an inability to sufficiently sequester the excess CDC20 protein. This allows the unsequestered APCCdc20 to promote anaphase, with mitotic slippage occurring as a result [174, 175]. However, it should be noted that while this is a possibility, enhanced APC activity and anaphase progression should, in the end, result in elevated targeting of CDC20 for degradation. A second mechanism of the APC overcoming SAC inhibition is through CDH1 activity. As the SAC cannot directly inhibit CDH1 activity, failure of the regulatory mechanisms that inhibit APC activation via CDH1 results in mitotic slippage, as APCCDH1 can prematurely target Securin for degradation [193, 194]. This occurs principally if Cyclin B1 activity is impeded, as CDK1Cyclin B1 phosphorylation of CDH1 prohibits binding to the APC. This dysfunction may occur if there is insufficient Cyclin B1 expressed during mitosis, or if there is a deficiency of ATP which is necessary for CDK1 to perform its phosphorylation events [286]. Aurora A, when in abundance, is also capable of inducing mitotic slippage through inhibition of SAC [218, 219].
Regulating S phase entrance
APCCDH1 plays a crucial role in regulating the entrance to S phase. During mitosis a failure to degrade the mitotic Cyclins A and B results in the proteins improperly accumulating in G1 and results in a premature promotion of S phase [75, 186]. APCCDH1 also directly regulates entry to S phase, in conjunction with the SCF. Depletion of CDH1 results in premature entry to S phase, as well as a prolonged S phase [66, 75, 182]. APCCDH1 and SCFCyclin F form a double negative feedback loop, where APCCDH1 targets Cyclin F for degradation, and SCFCyclinF targets CDH1 for degradation [67]. Coupled with the negative feedback loop of APCCDH1 autoubiquitination of CDH1 [189], expression of Cyclin F and formation of SCFCyclin F during G1 reaches a critical point of CDH1 depletion where APCCDH1 activity is unable to prevent full SCFCyclin F activity and the subsequent transition to S phase. Knockout of Cyclin F using siRNA resulted in a prolonged G1, however simultaneous siRNA knockout of CDH1 reversed this phenotype [67]. The timed degradation of CDH1 created by this mechanism permits a regulated entry to S phase, as loss of APCCDH1 activity results in the accumulation of Cyclin A [67]. APCCDH1 also polyubiquitinates the SCF subunit SKP2 for degradation to prevent cell cycle progression [32, 183]. APCCDH1 can also delay entry to S phase via polyubiquitination and subsequent degradation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) associated PAF15 [111].
Inducing cell cycle arrest
The APCCDH1 complex can initiate cell cycle arrest at multiple stages of the cell cycle [186]. At the G2/M transition, APCCDH1 acts in conjunction with CDC14B and PLK1 to prevent progression into mitosis in the event of DNA damage [177]. In response to DNA damage that occurs during the G2/M transition, the phosphatase CDC14B translocates to the nucleoplasm from the nucleolus and activates APCCDH1 via removal of inhibitory phosphorylation events blocking recruitment of CDH1 to the APC. APCCDH1 will then target PLK1 for degradation, resulting in transient stabilization of Claspin, a protein required for the initiation of DNA repair pathways [177]. Once the checkpoint is satisfied, phosphorylation of Claspin by residual PLK targets it for SCFβ-TrCP-mediated degradation [297–299]. Under normal conditions, it has been shown that Claspin is targeted by ACPCDH1 during G1 [177].
Genotoxic stress is not the only stressor that activates cell cycle arrest through the APC. Nutrient stresses also activate cell cycle arrest through the APC [16, 186, 260]. In CDH1-/- chicken cells (DT40) rapamycin is unable to induce G1 cell cycle arrest [186]. This is a result of altered CDK2 and retinoblastoma (Rb) pathways. Upon rapamycin treatment, wild type cells lose Rb phosphorylation, allowing the induction of G1 arrest, but in CDH1-/- cells, Rb phosphorylation is maintained with continued cell cycle progression [186]. In S. cerevisiae, Cdh1 acts to protect the cell from ethanol, caffeine, and hyperosmotic stress, as yeast cells lacking CDH1 still progress through the cell cycle, but are sensitive to multiple stresses [16]. The stress sensitivity appears to be due to elevated stability of Clb2 (orthologous to human Cyclin B2) and Hsl1 (ortholog of human NIM1-related Kinase) from a partially impaired APC that continues to drive cells through the G2/M transition despite the incurred cellular damage. Meanwhile, inhibition of the APC in quiescent cells drives their return to the cell cycle [26, 260]. This indicates that APC activity is required both for entrance to, and maintenance of, cell cycle arrest.
Acetylation of both CDC20 and CDH1 are key regulatory events impacting APC activity, as it prevents their respective bindings to the APC [65]. A lack of deacetylation of these APC coactivators, due to loss of the SIRT2 deacetylase, leads to elevated APC inhibition and lack of target degradation. This ultimately results in enhanced abundance of APC substrates, abnormal amplification of centrosomes, increased aneuploidy events and eventually mitotic catastrophe [65]. Studies in S. cerevisiae have revealed the complicated networks that the deacetylation enzyme Sir2, the yeast orthologue of SIRT2, impacts. Sir2 is an important stress response and longevity protein in S. cerevisiae, and it is tightly connected with a stress response network that interacts with the APC, namely the Fkh1 and Fkh2 Fox transcription factors [103, 104, 300]. In S. cerevisiae, under stress conditions, the APC and Fkhs work together to induce a response to stress [18, 20, 24]. Furthermore, when stress is encountered, Sir2 is recruited to Clb2 promoters in a Fkh1-dependent manner to repress CLB2 expression and stall the cell cycle [300]. Therefore, SIRT2 may be part of the mammalian APC stress response network, and thus a key regulator of the cell cycle.
APC subunit mutation
The notion that the APC is primarily important for cell health and avoidance of cancer progression suggests that loss of APC subunits may be linked to cancer development or progression. However, complete loss of APC function in animals is lethal [287, 301]. With this in mind it is not surprising that APC subunit mutations are rarely reported in animal and cell systems [302]. Nonetheless, APC subunit mutations have been reported, as briefly discussed above. For example, APC5 and APC7 were shown to interact with the CBP/p300 transcriptional activator, a histone acetyltransferase, and to play a direct role in transcriptional activation [303]. CBP/p300 is targeted by E1A to induce tumorigenic transformation. Further analysis showed that overexpression of APC5 or APC7 suppressed the transformative ability of E1A, while knockdown of APC5 or APC7 in vitro resulted in enhanced transformation, highlighting the role of the APC in stalling tumor transformation. Other studies have shown that APC7, and APC16 (subunits not observed in yeast) form a complex with APC3 [304]. Deletion of APC7 or APC16 in HCT116 colon cancer cells, however, revealed no overt phenotypes other than reduced in vitro ubiquitination activity [57]. These studies showed, nonetheless, that in APC7 or APC16 deletion cells, ablation of the essential MAD2 was tolerated. These cells had accelerated mitosis, no longer responded to SAC activity, and sustained increased genomic instability. The importance of APC7 was further suggested when 108 invasive ductal breast carcinomas were stained for APC7 expression [305]. It was reported that loss of APC7 was predominantly found in cases with poor prognosis or signs of malignancy. In other studies, it was found that Rothman-Thomson Syndrome Type 1, which causes juvenile cataracts, is due to a premature stop codon in APC1, resulting in reduced, but not complete loss of APC1 protein [306]. Additional studies revealed mutations in CDC16 and CDC23 in human colon cancer cells [56]. Interestingly, opposed to studies showing loss of APC subunit functions in many cancers, increased APC11 mRNA was observed in colorectal cancer samples, and correlated with worse overall survival [307]. APC11 is the APC catalytic subunit, so it remains a question as to why this subunit would behave differently than the other subunits studied in regards to cancer. Taken together, the bulk of the evidence indicates that mutations to variety of APC subunits confers a risk for disease onset.
Conclusions
Through its interactions with numerous cellular pathways, the APC maintains a complicated position in cancer development. While bound to CDC20, it acts in an oncogenic fashion and promotes tumor development; however, when bound to CDH1, the APC displays many tumor suppressive effects (Figure 4). Many genes encoding protein substrates normally degraded by APC E3 activity are found to be overabundant in a wide variety of cancers. Furthermore, many of the phenotypes associated with defective APC activity, such as elevated genomic instability, improperly regulated cell cycle, and aneuploidy, contribute to tumor progression and drug resistance. This suggests that activation of the APC, as previously suggested for prolonging lifespan [23], may also be relevant for treating cancer. Targeting APC activity has shown promise in an anti-tumor capacity, as the SAC inhibitors M2I-1 and TTKi, which both disrupt CDC20-SAC interactions, increase APCCDC20 activity and provide increased killing of cancer cells [31, 58–62]. In our current work we have observed loss of APC activity in canines with drug resistant lymphoma, and that increased APC activity was associated with remission, and APC activity loss again occurred when the animal relapsed (Arnason et al. under review). Furthermore, loss of SIRT2 and the resulting impaired activity in both APCCDH1 and APCCDC20 complexes, or the loss of CDH1 itself, promotes genomic instability and tumor progression [65], indicating that generalized APC dysfunction is tumorigenic [26–31]. Moreover, numerous reports have now identified a signature of overexpressed genes that encode APC substrates and inhibitors in a variety of aggressive tumors [37, 47]. Taken together, this provides a compelling rationale to further research directed at the role the APC plays in tumoral development.
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge Dr. Chris Eskiw for careful reading of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest to report.
Funding
Drs. Harkness and Arnason are funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada.
References
-
1.
Fouad YA, Aanei C. Revisiting the hallmarks of cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2017; 7:1016–36. [PubMed]
-
2.
Yazinski SA, Zou L. Functions, regulation, and therapeutic implications of the ATR checkpoint pathway. Annu Rev Genet. 2016; 50:155–73. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-genet-121415-121658 [PubMed]
-
3.
Potapova TA, Zhu J, Li R. Aneuploidy and chromosomal instability: a vicious cycle driving cellular evolution and cancer genome chaos. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2013; 32:377–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-013-9436-6 [PubMed]
-
4.
Carr MI, Jones SN. Regulation of the Mdm2-p53 signaling axis in the DNA damage response and tumorigenesis. Transl Cancer Res. 2016; 5:707–24. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr.2016.11.75 [PubMed]
-
5.
Kaina B. DNA damage-triggered apoptosis: critical role of DNA repair, double-strand breaks, cell proliferation and signaling. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003; 66:1547–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-2952(03)00510-0 [PubMed]
-
6.
Nogueira A, Fernandes M, Catarino R, Medeiros R. RAD52 functions in homologous recombination and its importance on genomic integrity maintenance and cancer therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2019; 11:1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers11111622 [PubMed]
-
7.
Fernald K, Kurokawa M. Evading apoptosis in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2013; 23:620–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2013.07.006 [PubMed]
-
8.
Wei M, Fabrizio P, Hu J, Ge H, Cheng C, Li L, Longo VD. Life span extension by calorie restriction depends on Rim15 and transcription factors downstream of ras/PKA, tor, and Sch9. PLoS Genet. 2008; 4:e13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.0040013 [PubMed]
-
9.
Wei M, Fabrizio P, Madia F, Hu J, Ge H, Li LM, Longo VD. Tor1/Sch9-regulated carbon source substitution is as effective as calorie restriction in life span extension. PLoS Genet. 2009; 5:e1000467. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000467 [PubMed]
-
10.
Madia F, Wei M, Yuan V, Hu J, Gattazzo C, Pham P, Goodman MF, Longo VD. Oncogene homologue Sch9 promotes age-dependent mutations by a superoxide and Rev1/polzeta-dependent mechanism. J Cell Biol. 2009; 186:509–23. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200906011 [PubMed]
-
11.
Smets B, Ghillebert R, De Snijder P, Binda M, Swinnen E, De Virgilio C, Winderickx J. Life in the midst of scarcity: adaptations to nutrient availability in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet. 2010; 56:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-009-0287-1 [PubMed]
-
12.
Lu JY, Lin YY, Sheu JC, Wu JT, Lee FJ, Chen Y, Lin MI, Chiang FT, Tai TY, Berger SL, Zhao Y, Tsai KS, Zhu H, et al. Acetylation of yeast AMPK controls intrinsic aging independently of caloric restriction. Cell. 2011; 146:969–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.044 [PubMed]
-
13.
Rodríguez-Colman MJ, Sorolla MA, Vall-Llaura N, Tamarit J, Ros J, Cabiscol E. The FOX transcription factor Hcm1 regulates oxidative metabolism in response to early nutrient limitation in yeast. Role of Snf1 and Tor1/Sch9 kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013; 1833:2004–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2013.02.015 [PubMed]
-
14.
Singh A, Chowdhury D, Gupta A, Meena RC, Chakrabarti A. TORC1-signalling is down-regulated in saccharomyces cerevisiae hsp30Δ cells by SNF1-dependent mechanisms. Yeast. 2018; 35:653–67. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.3360 [PubMed]
-
15.
Searle JS, Schollaert KL, Wilkins BJ, Sanchez Y. The DNA damage checkpoint and PKA pathways converge on APC substrates and Cdc20 to regulate mitotic progression. Nat Cell Biol. 2004; 6:138–45. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1092 [PubMed]
-
16.
Simpson-Lavy KJ, Sajman J, Zenvirth D, Brandeis M. APC/CCdh1 specific degradation of Hsl1 and Clb2 is required for proper stress responses of S. Cerevisiae. Cell Cycle. 2009; 8:3003–09. [PubMed]
-
17.
Rodríguez-Sánchez L, Rodríguez-López M, García Z, Tenorio-Gómez M, Schvartzman JB, Krimer DB, Hernández P. The fission yeast rDNA-binding protein Reb1 regulates G1 phase under nutritional stress. J Cell Sci. 2011; 124:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.070987 [PubMed]
-
18.
Postnikoff SD, Malo ME, Wong B, Harkness TA. The yeast forkhead transcription factors fkh1 and fkh2 regulate lifespan and stress response together with the anaphase-promoting complex. PLoS Genet. 2012; 8:e1002583. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1002583 [PubMed]
-
19.
Menzel J, Malo ME, Chan C, Prusinkiewicz M, Arnason TG, Harkness TA. The anaphase promoting complex regulates yeast lifespan and rDNA stability by targeting Fob1 for degradation. Genetics. 2014; 196:693–709. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.113.158949 [PubMed]
-
20.
Malo ME, Postnikoff SD, Arnason TG, Harkness TA. Mitotic degradation of yeast Fkh1 by the anaphase promoting complex is required for normal longevity, genomic stability and stress resistance. Aging (Albany NY). 2016; 8:810–30. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.100949 [PubMed]
-
21.
Atalay PB, Asci O, Kaya FO, Tuna BG. Hydrogen peroxide prolongs mitotic arrest in a dose dependent manner and independently of the spindle assembly checkpoint activity in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Acta Biol Hung. 2017; 68:477–89. https://doi.org/10.1556/018.68.2017.4.12 [PubMed]
-
22.
Rubio A, García-Blanco N, Vázquez-Bolado A, Belén Suárez M, Moreno S. Nutritional cell cycle reprogramming reveals that inhibition of Cdk1 is required for proper MBF-dependent transcription. J Cell Sci. 2018; 131:jcs218743. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.218743 [PubMed]
-
23.
Harkness TA. Activating the anaphase promoting complex to enhance genomic stability and prolong lifespan. Int J Mol Sci. 2018; 19:1888. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071888 [PubMed]
-
24.
Postnikoff SD, Harkness TA. Mechanistic insights into aging, cell-cycle progression, and stress response. Front Physiol. 2012; 3:183. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2012.00183 [PubMed]
-
25.
Cappell SD, Mark KG, Garbett D, Pack LR, Rape M, Meyer T. EMI1 switches from being a substrate to an inhibitor of APC/CCDH1 to start the cell cycle. Nature. 2018; 558:313–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0199-7 [PubMed]
-
26.
Cappell SD, Chung M, Jaimovich A, Spencer SL, Meyer T. Irreversible APCCdh1 inactivation underlies the point of no return for cell-cycle entry. Cell. 2016; 166:167–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.077 [PubMed]
-
27.
Bellanger S, Blachon S, Mechali F, Bonne-Andrea C, Thierry F. High-risk but not low-risk HPV E2 proteins bind to the APC activators Cdh1 and Cdc20 and cause genomic instability. Cell Cycle. 2005; 4:1608–15. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.4.11.2123 [PubMed]
-
28.
Kucharski TJ, Minshall PE, Moustafa-Kamal M, Turnell AS, Teodoro JG. Reciprocal regulation between 53BP1 and the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome is required for genomic stability during mitotic stress. Cell Rep. 2017; 18:1982–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.01.080 [PubMed]
-
29.
Garzón J, Rodríguez R, Kong Z, Chabes A, Rodríguez-Acebes S, Méndez J, Moreno S, García-Higuera I. Shortage of dNTPs underlies altered replication dynamics and DNA breakage in the absence of the APC/C cofactor Cdh1. Oncogene. 2017; 36:5808–18. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.186 [PubMed]
-
30.
Sansregret L, Patterson JO, Dewhurst S, López-García C, Koch A, McGranahan N, Chao WC, Barry DJ, Rowan A, Instrell R, Horswell S, Way M, Howell M, et al. APC/C dysfunction limits excessive cancer chromosomal instability. Cancer Discov. 2017; 7:218–33. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0645 [PubMed]
-
31.
Thu KL, Silvester J, Elliott MJ, Ba-Alawi W, Duncan MH, Elia AC, Mer AS, Smirnov P, Safikhani Z, Haibe-Kains B, Mak TW, Cescon DW. Disruption of the anaphase-promoting complex confers resistance to TTK inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018; 115:E1570–77. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1719577115 [PubMed]
-
32.
Zhou Z, He M, Shah AA, Wan Y. Insights into APC/C: from cellular function to diseases and therapeutics. Cell Div. 2016; 11:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13008-016-0021-6 [PubMed]
-
33.
Visintin R, Prinz S, Amon A. CDC20 and CDH1: a family of substrate-specific activators of APC-dependent proteolysis. Science. 1997; 278:460–63. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.278.5337.460 [PubMed]
-
34.
Sivakumar S, Gorbsky GJ. Spatiotemporal regulation of the anaphase-promoting complex in mitosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015; 16:82–94. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3934 [PubMed]
-
35.
Li J, Gao JZ, Du JL, Huang ZX, Wei LX. Increased CDC20 expression is associated with development and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2014; 45:1547–55. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2014.2559 [PubMed]
-
36.
Mao Y, Li K, Lu L, Si-Tu J, Lu M, Gao X. Overexpression of Cdc20 in clinically localized prostate cancer: relation to high gleason score and biochemical recurrence after laparoscopic radical prostatectomy. Cancer Biomark. 2016; 16:351–58. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-160573 [PubMed]
-
37.
Zhang Y, Li J, Yi K, Feng J, Cong Z, Wang Z, Wei Y, Wu F, Cheng W, Samo AA, Salomoni P, Yang Q, Huang Y, et al. Elevated signature of a gene module coexpressed with CDC20 marks genomic instability in glioma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2019; 116:6975–84. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1814060116 [PubMed]
-
38.
Schrock MS, Stromberg BR, Scarberry L, Summers MK. APC/C ubiquitin ligase: functions and mechanisms in tumorigenesis. Semin Cancer Biol. 2020; S1044-579X:30059–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.03.001 [PubMed]
-
39.
Rahimi H, Ahmadzadeh A, Yousef-amoli S, Kokabee L, Shokrgozar MA, Mahdian R, Karimipoor M. The expression pattern of APC2 and APC7 in various cancer cell lines and AML patients. Adv Med Sci. 2015; 60:259–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advms.2015.04.007 [PubMed]
-
40.
Zhou J, Zhang S, Fu G, He Z, Xu Y, Ye W, Chen Z. Overexpression of APC11 predicts worse survival in lung adenocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2018; 11:7125–32. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S177252 [PubMed]
-
41.
Taniguchi K, Momiyama N, Ueda M, Matsuyama R, Mori R, Fujii Y, Ichikawa Y, Endo I, Togo S, Shimada H. Targeting of CDC20 via small interfering RNA causes enhancement of the cytotoxicity of chemoradiation. Anticancer Res. 2008; 28:1559–63. [PubMed]
-
42.
Wang L, Zhang J, Wan L, Zhou X, Wang Z, Wei W. Targeting Cdc20 as a novel cancer therapeutic strategy. Pharmacol Ther. 2015; 151:141–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2015.04.002 [PubMed]
-
43.
Lub S, Maes A, Maes K, De Veirman K, De Bruyne E, Menu E, Fostier K, Kassambara A, Moreaux J, Hose D, Leleu X, King RW, Vanderkerken K, Van Valckenborgh E. Inhibiting the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome induces a metaphase arrest and cell death in multiple myeloma cells. Oncotarget. 2016; 7:4062–76. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6768 [PubMed]
-
44.
Gao Y, Zhang B, Wang Y, Shang G. Cdc20 inhibitor apcin inhibits the growth and invasion of osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2018; 40:841–48. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6467 [PubMed]
-
45.
de Lange J, Faramarz A, Oostra AB, de Menezes RX, van der Meulen IH, Rooimans MA, Rockx DA, Brakenhoff RH, van Beusechem VW, King RW, de Winter JP, Wolthuis RM. Defective sister chromatid cohesion is synthetically lethal with impaired APC/C function. Nat Commun. 2015; 6:8399. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9399 [PubMed]
-
46.
Schuyler SC, Wu YO, Chen HY, Ding YS, Lin CJ, Chu YT, Chen TC, Liao L, Tsai WW, Huang A, Wang LI, Liao TW, Jhuo JH, Cheng V. Peptide inhibitors of the anaphase promoting-complex that cause sensitivity to microtubule poison. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0198930. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198930 [PubMed]
-
47.
Lehman NL, Tibshirani R, Hsu JY, Natkunam Y, Harris BT, West RB, Masek MA, Montgomery K, van de Rijn M, Jackson PK. Oncogenic regulators and substrates of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome are frequently overexpressed in Malignant tumors. Am J Pathol. 2007; 170:1793–805. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2007.060767 [PubMed]
-
48.
Schmit TL, Ledesma MC, Ahmad N. Modulating polo-like kinase 1 as a means for cancer chemoprevention. Pharm Res. 2010; 27:989–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11095-010-0051-8 [PubMed]
-
49.
Karra H, Repo H, Ahonen I, Löyttyniemi E, Pitkänen R, Lintunen M, Kuopio T, Söderström M, Kronqvist P. Cdc20 and securin overexpression predict short-term breast cancer survival. Br J Cancer. 2014; 110:2905–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2014.252 [PubMed]
-
50.
Heredia FF, de Sousa JC, Ribeiro Junior HL, Carvalho AF, Magalhaes SM, Pinheiro RF. Proteins related to the spindle and checkpoint mitotic emphasize the different pathogenesis of hypoplastic MDS. Leuk Res. 2014; 38:218–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2013.11.003 [PubMed]
-
51.
Zhang N, Pati D. Biology and insights into the role of cohesin protease separase in human Malignancies. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 2017; 92:2070–83. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12321 [PubMed]
-
52.
Pérez de Castro I, de Cárcer G, Malumbres M. A census of mitotic cancer genes: new insights into tumor cell biology and cancer therapy. Carcinogenesis. 2007; 28:899–912. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgm019 [PubMed]
-
53.
Komlodi-Pasztor E, Sackett DL, Fojo AT. Inhibitors targeting mitosis: tales of how great drugs against a promising target were brought down by a flawed rationale. Clin Cancer Res. 2012; 18:51–63. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0999 [PubMed]
-
54.
Dominguez-Brauer C, Thu KL, Mason JM, Blaser H, Bray MR, Mak TW. Targeting mitosis in cancer: emerging strategies. Mol Cell. 2015; 60:524–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.11.006 [PubMed]
-
55.
Gutteridge RE, Ndiaye MA, Liu X, Ahmad N. Plk1 inhibitors in cancer therapy: from laboratory to clinics. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016; 15:1427–35. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0897 [PubMed]
-
56.
Wang Q, Moyret-Lalle C, Couzon F, Surbiguet-Clippe C, Saurin JC, Lorca T, Navarro C, Puisieux A. Alterations of anaphase-promoting complex genes in human colon cancer cells. Oncogene. 2003; 22:1486–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206224 [PubMed]
-
57.
Wild T, Budzowska M, Hellmuth S, Eibes S, Karemore G, Barisic M, Stemmann O, Choudhary C. Deletion of APC7 or APC16 allows proliferation of human cells without the spindle assembly checkpoint. Cell Rep. 2018; 25:2317–28.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2018.10.104 [PubMed]
-
58.
Kastl J, Braun J, Prestel A, Möller HM, Huhn T, Mayer TU. Mad2 inhibitor-1 (M2I-1): a small molecule protein-protein interaction inhibitor targeting the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint. ACS Chem Biol. 2015; 10:1661–66. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.5b00121 [PubMed]
-
59.
Libouban MA, de Roos JA, Uitdehaag JC, Willemsen-Seegers N, Mainardi S, Dylus J, de Man J, Tops B, Meijerink JP, Storchová Z, Buijsman RC, Medema RH, Zaman GJ. Stable aneuploid tumors cells are more sensitive to TTK inhibition than chromosomally unstable cell lines. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:38309–25. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.16213 [PubMed]
-
60.
Zaman GJ, de Roos JA, Libouban MA, Prinsen MB, de Man J, Buijsman RC, Uitdehaag JC. TTK inhibitors as a targeted therapy for CTNNB1 (β-catenin) mutant cancers. Mol Cancer Ther. 2017; 16:2609–17. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0342 [PubMed]
-
61.
Maia AR, Linder S, Song JY, Vaarting C, Boon U, Pritchard CE, Velds A, Huijbers IJ, van Tellingen O, Jonkers J, Medema RH. Mps1 inhibitors synergise with low doses of taxanes in promoting tumour cell death by enhancement of errors in cell division. Br J Cancer. 2018; 118:1586–95. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41416-018-0081-2 [PubMed]
-
62.
Li J, Dang N, Martinez-Lopez N, Jowsey PA, Huang D, Lightowlers RN, Gao F, Huang JY. M2I-1 disrupts the in vivo interaction between CDC20 and MAD2 and increases the sensitivities of cancer cell lines to anti-mitotic drugs via MCL-1s. Cell Div. 2019; 14:5. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13008-019-0049-5 [PubMed]
-
63.
Kapanidou M, Curtis NL, Bolanos-Garcia VM. Cdc20: at the crossroads between chromosome segregation and mitotic exit. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017; 42:193–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2016.12.001 [PubMed]
-
64.
Engelbert D, Schnerch D, Baumgarten A, Wäsch R. The ubiquitin ligase APC(Cdh1) is required to maintain genome integrity in primary human cells. Oncogene. 2008; 27:907–17. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210703 [PubMed]
-
65.
Kim HS, Vassilopoulos A, Wang RH, Lahusen T, Xiao Z, Xu X, Li C, Veenstra TD, Li B, Yu H, Ji J, Wang XW, Park SH, et al. SIRT2 maintains genome integrity and suppresses tumorigenesis through regulating APC/C activity. Cancer Cell. 2011; 20:487–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2011.09.004 [PubMed]
-
66.
García-Higuera I, Manchado E, Dubus P, Cañamero M, Méndez J, Moreno S, Malumbres M. Genomic stability and tumour suppression by the APC/C cofactor Cdh1. Nat Cell Biol. 2008; 10:802–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1742 [PubMed]
-
67.
Choudhury R, Bonacci T, Arceci A, Lahiri D, Mills CA, Kernan JL, Branigan TB, DeCaprio JA, Burke DJ, Emanuele MJ. APC/C and SCFcyclin F constitute a reciprocal feedback circuit controlling S-phase entry. Cell Rep. 2016; 16:3359–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.08.058 [PubMed]
-
68.
Simpson-Lavy KJ, Brandeis M. Clb2 and the APC/C(Cdh1) regulate Swe1 stability. Cell Cycle. 2010; 9:3046–53. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc..9.115.12457 [PubMed]
-
69.
Simpson-Lavy KJ, Oren YS, Feine O, Sajman J, Listovsky T, Brandeis M. Fifteen years of APC/cyclosome: a short and impressive biography. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010; 38:78–82. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0380078 [PubMed]
-
70.
Harley ME, Allan LA, Sanderson HS, Clarke PR. Phosphorylation of mcl-1 by CDK1-cyclin B1 initiates its Cdc20-dependent destruction during mitotic arrest. EMBO J. 2010; 29:2407–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2010.112 [PubMed]
-
71.
Wan L, Tan M, Yang J, Inuzuka H, Dai X, Wu T, Liu J, Shaik S, Chen G, Deng J, Malumbres M, Letai A, Kirschner MW, et al. APCCdc20 suppresses apoptosis through targeting bim for ubiquitination and destruction. Dev Cell. 2014; 29:377–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2014.04.022 [PubMed]
-
72.
Ding Y, Yu S, Bao Z, Liu Y, Liang T. CDC20 with Malignant progression and poor prognosis of astrocytoma revealed by analysis on gene expression. J Neurooncol. 2017; 133:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2434-8 [PubMed]
-
73.
Wu F, Dai X, Gan W, Wan L, Li M, Mitsiades N, Wei W, Ding Q, Zhang J. Prostate cancer-associated mutation in SPOP impairs its ability to target Cdc20 for poly-ubiquitination and degradation. Cancer Lett. 2017; 385:207–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2016.10.021 [PubMed]
-
74.
Chang DZ, Ma Y, Ji B, Liu Y, Hwu P, Abbruzzese JL, Logsdon C, Wang H. Increased CDC20 expression is associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma differentiation and progression. J Hematol Oncol. 2012; 5:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-8722-5-15 [PubMed]
-
75.
Krohs J, Schnerch D, Follo M, Felthaus J, Engelhardt M, Wäsch RM. The tumor suppressor APC/CCdh1 and its role in replication stress and the origin of genomic instability. Blood. 2013; 122:2489–2489. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood.V122.21.2489.2489
-
76.
Greil C, Krohs J, Schnerch D, Follo M, Felthaus J, Engelhardt M, Wäsch R. The role of APC/CCdh1 in replication stress and origin of genomic instability. Oncogene. 2016; 35:3062–70. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.367 [PubMed]
-
77.
Matyskiela ME, Morgan DO. Analysis of activator-binding sites on the APC/C supports a cooperative substrate-binding mechanism. Mol Cell. 2009; 34:68–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.02.027 [PubMed]
-
78.
Ahlskog JK, Björk JK, Elsing AN, Aspelin C, Kallio M, Roos-Mattjus P, Sistonen L. Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome participates in the acute response to protein-damaging stress. Mol Cell Biol. 2010; 30:5608–20. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01506-09 [PubMed]
-
79.
Menssen A, Epanchintsev A, Lodygin D, Rezaei N, Jung P, Verdoodt B, Diebold J, Hermeking H. c-MYC delays prometaphase by direct transactivation of MAD2 and BubR1: identification of mechanisms underlying c-MYC-induced DNA damage and chromosomal instability. Cell Cycle. 2007; 6:339–52. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.6.3.3808 [PubMed]
-
80.
O’Donovan KJ, Diedler J, Couture GC, Fak JJ, Darnell RB. The onconeural antigen cdr2 is a novel APC/C target that acts in mitosis to regulate c-myc target genes in mammalian tumor cells. PLoS One. 2010; 5:e10045. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0010045 [PubMed]
-
81.
Ji Z, Gao H, Jia L, Li B, Yu H. A sequential multi-target Mps1 phosphorylation cascade promotes spindle checkpoint signaling. Elife. 2017; 6:e22513. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.22513 [PubMed]
-
82.
Keller JA, Petty EM. CHFR binds to and regulates MAD2 in the spindle checkpoint through its cysteine-rich domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011; 409:389–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.04.143 [PubMed]
-
83.
Yang X, Xu W, Hu Z, Zhang Y, Xu N. Chk1 is required for the metaphase-anaphase transition via regulating the expression and localization of Cdc20 and Mad2. Life Sci. 2014; 106:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2014.04.011 [PubMed]
-
84.
Yamada M, Watanabe K, Mistrik M, Vesela E, Protivankova I, Mailand N, Lee M, Masai H, Lukas J, Bartek J. ATR-Chk1-APC/CCdh1-dependent stabilization of Cdc7-ASK (Dbf4) kinase is required for DNA lesion bypass under replication stress. Genes Dev. 2013; 27:2459–72. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.224568.113 [PubMed]
-
85.
Zhang WN, Zhou J, Zhou T, Li AL, Wang N, Xu JJ, Chang Y, Man JH, Pan X, Li T, Li WH, Mu R, Liang B, et al. Phosphorylation-triggered CUEDC2 degradation promotes UV-induced G1 arrest through APC/CCdh1 regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013; 110:11017–22. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1221009110 [PubMed]
-
86.
Lee YJ, Lee HJ, Lee JS, Jeoung D, Kang CM, Bae S, Lee SJ, Kwon SH, Kang D, Lee YS. A novel function for HSF1-induced mitotic exit failure and genomic instability through direct interaction between HSF1 and Cdc20. Oncogene. 2008; 27:2999–3009. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210966 [PubMed]
-
87.
Sako K, Suzuki K, Isoda M, Yoshikai S, Senoo C, Nakajo N, Ohe M, Sagata N. Emi2 mediates meiotic MII arrest by competitively inhibiting the binding of Ube2S to the APC/C. Nat Commun. 2014; 5:3667. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4667 [PubMed]
-
88.
Shoji S, Muto Y, Ikeda M, He F, Tsuda K, Ohsawa N, Akasaka R, Terada T, Wakiyama M, Shirouzu M, Yokoyama S. The zinc-binding region (ZBR) fragment of Emi2 can inhibit APC/C by targeting its association with the coactivator Cdc20 and UBE2C-mediated ubiquitylation. FEBS Open Bio. 2014; 4:689–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fob.2014.06.010 [PubMed]
-
89.
Kwan PS, Lau CC, Chiu YT, Man C, Liu J, Tang KD, Wong YC, Ling MT. Daxx regulates mitotic progression and prostate cancer predisposition. Carcinogenesis. 2013; 34:750–59. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgs391 [PubMed]
-
90.
Kaisari S, Sitry-Shevah D, Miniowitz-Shemtov S, Teichner A, Hershko A. Role of CCT chaperonin in the disassembly of mitotic checkpoint complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017; 114:956–61. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1620451114 [PubMed]
-
91.
Camasses A, Bogdanova A, Shevchenko A, Zachariae W. The CCT chaperonin promotes activation of the anaphase-promoting complex through the generation of functional Cdc20. Mol Cell. 2003; 12:87–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00244-2 [PubMed]
-
92.
Wang K, Sturt-Gillespie B, Hittle JC, Macdonald D, Chan GK, Yen TJ, Liu ST. Thyroid hormone receptor interacting protein 13 (TRIP13) AAA-ATPase is a novel mitotic checkpoint-silencing protein. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289:23928–37. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.585315 [PubMed]
-
93.
Ellederova Z, Del Rincon S, Koncicka M, Susor A, Kubelka M, Sun D, Spruck C. CKS1 germ line exclusion is essential for the transition from meiosis to early embryonic development. Mol Cell Biol. 2019; 39:e00590–18. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00590-18 [PubMed]
-
94.
Gao YF, Li T, Chang Y, Wang YB, Zhang WN, Li WH, He K, Mu R, Zhen C, Man JH, Pan X, Li T, Chen L, et al. Cdk1-phosphorylated CUEDC2 promotes spindle checkpoint inactivation and chromosomal instability. Nat Cell Biol. 2011; 13:924–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2287 [PubMed]
-
95.
Kim AH, Puram SV, Bilimoria PM, Ikeuchi Y, Keough S, Wong M, Rowitch D, Bonni A. A centrosomal Cdc20-APC pathway controls dendrite morphogenesis in postmitotic neurons. Cell. 2009; 136:322–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.11.050 [PubMed]
-
96.
Coster G, Hayouka Z, Argaman L, Strauss C, Friedler A, Brandeis M, Goldberg M. The DNA damage response mediator MDC1 directly interacts with the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:32053–64. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M705890200 [PubMed]
-
97.
Townsend K, Mason H, Blackford AN, Miller ES, Chapman JR, Sedgwick GG, Barone G, Turnell AS, Stewart GS. Mediator of DNA damage checkpoint 1 (MDC1) regulates mitotic progression. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284:33939–48. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.009191 [PubMed]
-
98.
Hatakeyama S. TRIM proteins and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2011; 11:792–804. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3139 [PubMed]
-
99.
Yu C, Ding Z, Liang H, Zhang B, Chen X. The roles of TIF1γ in cancer. Front Oncol. 2019; 9:979. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00979 [PubMed]
-
100.
Sedgwick GG, Townsend K, Martin A, Shimwell NJ, Grand RJ, Stewart GS, Nilsson J, Turnell AS. Transcriptional intermediary factor 1γ binds to the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome and promotes mitosis. Oncogene. 2013; 32:4622–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.501 [PubMed]
-
101.
Bembenek J, Yu H. Regulation of the anaphase-promoting complex by the dual specificity phosphatase human Cdc14a. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:48237–42. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M108126200 [PubMed]
-
102.
Fu AK, Hung KW, Fu WY, Shen C, Chen Y, Xia J, Lai KO, Ip NY. APCCdh1 mediates EphA4-dependent downregulation of AMPA receptors in homeostatic plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2011; 14:181–89. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2715 [PubMed]
-
103.
Berdichevsky A, Guarente L. A stress response pathway involving sirtuins, forkheads and 14-3-3 proteins. Cell Cycle. 2006; 5:2588–91. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.5.22.3513 [PubMed]
-
104.
Wierman MB, Smith JS. Yeast sirtuins and the regulation of aging. FEMS Yeast Res. 2014; 14:73–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/1567-1364.12115 [PubMed]
-
105.
Gong Y, Zack TI, Morris LG, Lin K, Hukkelhoven E, Raheja R, Tan IL, Turcan S, Veeriah S, Meng S, Viale A, Schumacher SE, Palmedo P, et al. Pan-cancer genetic analysis identifies PARK2 as a master regulator of G1/S cyclins. Nat Genet. 2014; 46:588–94. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2981 [PubMed]
-
106.
Lee SB, Kim JJ, Nam HJ, Gao B, Yin P, Qin B, Yi SY, Ham H, Evans D, Kim SH, Zhang J, Deng M, Liu T, et al. Parkin regulates mitosis and genomic stability through Cdc20/Cdh1. Mol Cell. 2015; 60:21–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.08.011 [PubMed]
-
107.
Bansal S, Tiwari S. Mechanisms for the temporal regulation of substrate ubiquitination by the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome. Cell Div. 2019; 14:14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13008-019-0057-5 [PubMed]
-
108.
Huang J, Bonni A. A decade of the anaphase-promoting complex in the nervous system. Genes Dev. 2016; 30:622–38. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.274324.115 [PubMed]
-
109.
Sedgwick GG, Hayward DG, Di Fiore B, Pardo M, Yu L, Pines J, Nilsson J. Mechanisms controlling the temporal degradation of Nek2A and Kif18A by the APC/C-Cdc20 complex. EMBO J. 2013; 32:303–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2012.335 [PubMed]
-
110.
Salsi V, Fantini S, Zappavigna V. NUP98 fusion oncoproteins interact with the APC/C(Cdc20) as a pseudosubstrate and prevent mitotic checkpoint complex binding. Cell Cycle. 2016; 15:2275–87. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2016.1172156 [PubMed]
-
111.
Emanuele MJ, Ciccia A, Elia AE, Elledge SJ. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-associated KIAA0101/PAF15 protein is a cell cycle-regulated anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2011; 108:9845–50. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1106136108 [PubMed]
-
112.
Cotto-Rios XM, Jones MJ, Busino L, Pagano M, Huang TT. APC/CCdh1-dependent proteolysis of USP1 regulates the response to UV-mediated DNA damage. J Cell Biol. 2011; 194:177–86. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201101062 [PubMed]
-
113.
Chow C, Wong N, Pagano M, Lun SW, Nakayama KI, Nakayama K, Lo KW. Regulation of APC/CCdc20 activity by RASSF1A-APC/CCdc20 circuitry. Oncogene. 2012; 31:1975–87. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2011.372 [PubMed]
-
114.
Paul D, Ghorai S, Dinesh US, Shetty P, Chattopadhyay S, Santra MK. Cdc20 directs proteasome-mediated degradation of the tumor suppressor SMAR1 in higher grades of cancer through the anaphase promoting complex. Cell Death Dis. 2017; 8:e2882. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.270 [PubMed]
-
115.
Rokudai S, Li Y, Otaka Y, Fujieda M, Owens DM, Christiano AM, Nishiyama M, Prives C. STXBP4 regulates APC/c-mediated p63 turnover and drives squamous cell carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018; 115:E4806–14. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1718546115 [PubMed]
-
116.
Lin Z, Tan C, Qiu Q, Kong S, Yang H, Zhao F, Liu Z, Li J, Kong Q, Gao B, Barrett T, Yang GY, Zhang J, Fang D. Ubiquitin-specific protease 22 is a deubiquitinase of CCNB1. Cell Discov. 2015; 1:15028. https://doi.org/10.1038/celldisc.2015.28 [PubMed]
-
117.
Li R, Wan B, Zhou J, Wang Y, Luo T, Gu X, Chen F, Yu L. APC/CCdh1 targets brain-specific kinase 2 (BRSK2) for degradation via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e45932. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045932 [PubMed]
-
118.
Chen H, Xu X, Wang G, Zhang B, Wang G, Xin G, Liu J, Jiang Q, Zhang H, Zhang C. CDK4 protein is degraded by anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome in mitosis and reaccumulates in early G1 phase to initiate a new cell cycle in HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 2017; 292:10131–41. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.773226 [PubMed]
-
119.
Yuan X, Srividhya J, De Luca T, Lee JH, Pomerening JR. Uncovering the role of APC-Cdh1 in generating the dynamics of s-phase onset. Mol Biol Cell. 2014; 25:441–56. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E13-08-0480 [PubMed]
-
120.
Pawar SA, Sarkar TR, Balamurugan K, Sharan S, Wang J, Zhang Y, Dowdy SF, Huang AM, Sterneck E. C/EBPδ targets cyclin D1 for proteasome-mediated degradation via induction of CDC27/APC3 expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010; 107:9210–15. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0913813107 [PubMed]
-
121.
Zhang J, Li H, Zhou T, Zhou J, Herrup K. Cdk5 levels oscillate during the neuronal cell cycle: Cdh1 ubiquitination triggers proteosome-dependent degradation during s-phase. J Biol Chem. 2012; 287:25985–94. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M112.343152 [PubMed]
-
122.
Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, et al. Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network. Nature. 2005; 437:1173–78. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04209 [PubMed]
-
123.
Horn SR, Thomenius MJ, Johnson ES, Freel CD, Wu JQ, Coloff JL, Yang CS, Tang W, An J, Ilkayeva OR, Rathmell JC, Newgard CB, Kornbluth S. Regulation of mitochondrial morphology by APC/CCdh1-mediated control of Drp1 stability. Mol Biol Cell. 2011; 22:1207–16. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E10-07-0567 [PubMed]
-
124.
Huang NJ, Zhang L, Tang W, Chen C, Yang CS, Kornbluth S. The Trim39 ubiquitin ligase inhibits APC/CCdh1-mediated degradation of the bax activator MOAP-1. J Cell Biol. 2012; 197:361–67. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201111141 [PubMed]
-
125.
Nourry C, Maksumova L, Pang M, Liu X, Wang T. Direct interaction between Smad3, APC10, CDH1 and HEF1 in proteasomal degradation of HEF1. BMC Cell Biol. 2004; 5:20. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2121-5-20 [PubMed]
-
126.
Lu L, Hu S, Wei R, Qiu X, Lu K, Fu Y, Li H, Xing G, Li D, Peng R, He F, Zhang L. The HECT type ubiquitin ligase NEDL2 is degraded by anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C)-Cdh1, and its tight regulation maintains the metaphase to anaphase transition. J Biol Chem. 2013; 288:35637–50. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.472076 [PubMed]
-
127.
von Klitzing C, Huss R, Illert AL, Fröschl A, Wötzel S, Peschel C, Bassermann F, Duyster J. APC/CCdh1-mediated degradation of the f-box protein NIPA is regulated by its association with Skp1. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e28998. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028998 [PubMed]
-
128.
Cao J, Dai X, Wan L, Wang H, Zhang J, Goff PS, Sviderskaya EV, Xuan Z, Xu Z, Xu X, Hinds P, Flaherty KT, Faller DV, et al. The E3 ligase APC/CCdh1 promotes ubiquitylation-mediated proteolysis of PAX3 to suppress melanocyte proliferation and melanoma growth. Sci Signal. 2015; 8:ra87. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aab1995 [PubMed]
-
129.
Choi BH, Pagano M, Huang C, Dai W. Cdh1, a substrate-recruiting component of anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) ubiquitin E3 ligase, specifically interacts with phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and promotes its removal from chromatin. J Biol Chem. 2014; 289:17951–59. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M114.559005 [PubMed]
-
130.
Dogan T, Gnad F, Chan J, Phu L, Young A, Chen MJ, Doll S, Stokes MP, Belvin M, Friedman LS, Kirkpatrick DS, Hoeflich KP, Hatzivassiliou G. Role of the E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF157 as a novel downstream effector linking PI3K and MAPK signaling pathways to the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 2017; 292:14311–24. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.792754 [PubMed]
-
131.
Kannan M, Lee SJ, Schwedhelm-Domeyer N, Stegmüller J. The E3 ligase Cdh1-anaphase promoting complex operates upstream of the E3 ligase Smurf1 in the control of axon growth. Development. 2012; 139:3600–12. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.081786 [PubMed]
-
132.
Stroschein SL, Bonni S, Wrana JL, Luo K. Smad3 recruits the anaphase-promoting complex for ubiquitination and degradation of SnoN. Genes Dev. 2001; 15:2822–36. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.912901 [PubMed]
-
133.
Jeng JC, Lin YM, Lin CH, Shih HM. Cdh1 controls the stability of TACC3. Cell Cycle. 2009; 8:3537–44. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.8.21.9935 [PubMed]
-
134.
Datta NS, Williams JL, Caldwell J, Curry AM, Ashcraft EK, Long MW. Novel alterations in CDK1/cyclin B1 kinase complex formation occur during the acquisition of a polyploid DNA content. Mol Biol Cell. 1996; 7:209–23. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.7.2.209 [PubMed]
-
135.
Rempel RE, Sleight SB, Maller JL. Maternal xenopus Cdk2-cyclin E complexes function during meiotic and early embryonic cell cycles that lack a G1 phase. J Biol Chem. 1995; 270:6843–55. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.270.12.6843 [PubMed]
-
136.
Bates S, Bonetta L, MacAllan D, Parry D, Holder A, Dickson C, Peters G. CDK6 (PLSTIRE) and CDK4 (PSK-J3) are a distinct subset of the cyclin-dependent kinases that associate with cyclin D1. Oncogene. 1994; 9:71–79. [PubMed]
-
137.
Puklowski A, Homsi Y, Keller D, May M, Chauhan S, Kossatz U, Grünwald V, Kubicka S, Pich A, Manns MP, Hoffmann I, Gönczy P, Malek NP. The SCF-FBXW5 E3-ubiquitin ligase is regulated by PLK4 and targets HsSAS-6 to control centrosome duplication. Nat Cell Biol. 2011; 13:1004–09. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb2282 [PubMed]
-
138.
Cui Y, Cheng X, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Li S, Wang C, Guadagno TM. Degradation of the human mitotic checkpoint kinase Mps1 is cell cycle-regulated by APC-cCdc20 and APC-cCdh1 ubiquitin ligases. J Biol Chem. 2010; 285:32988–98. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.140905 [PubMed]
-
139.
Lim HJ, Dimova NV, Tan MK, Sigoillot FD, King RW, Shi Y. The G2/M regulator histone demethylase PHF8 is targeted for degradation by the anaphase-promoting complex containing CDC20. Mol Cell Biol. 2013; 33:4166–80. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00689-13 [PubMed]
-
140.
Mosbech A, Gibbs-Seymour I, Kagias K, Thorslund T, Beli P, Povlsen L, Nielsen SV, Smedegaard S, Sedgwick G, Lukas C, Hartmann-Petersen R, Lukas J, Choudhary C, et al. DVC1 (C1orf124) is a DNA damage-targeting p97 adaptor that promotes ubiquitin-dependent responses to replication blocks. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012; 19:1084–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2395 [PubMed]
-
141.
Boulay K, Ghram M, Viranaicken W, Trépanier V, Mollet S, Fréchina C, DesGroseillers L. Cell cycle-dependent regulation of the RNA-binding protein Staufen1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014; 42:7867–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku506 [PubMed]
-
142.
Ichim G, Mola M, Finkbeiner MG, Cros MP, Herceg Z, Hernandez-Vargas H. The histone acetyltransferase component TRRAP is targeted for destruction during the cell cycle. Oncogene. 2014; 33:181–92. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.570 [PubMed]
-
143.
Bonacci T, Suzuki A, Grant GD, Stanley N, Cook JG, Brown NG, Emanuele MJ. cezanne/OTUD7B is a cell cycle-regulated deubiquitinase that antagonizes the degradation of APC/C substrates. EMBO J. 2018; 37:e98701. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201798701 [PubMed]
-
144.
Glotzer M, Murray AW, Kirschner MW. Cyclin is degraded by the ubiquitin pathway. Nature. 1991; 349:132–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/349132a0 [PubMed]
-
145.
Pfleger CM, Kirschner MW. The KEN box: an APC recognition signal distinct from the D box targeted by Cdh1. Genes Dev. 2000; 14:655–65. [PubMed]
-
146.
Kraft C, Vodermaier HC, Maurer-Stroh S, Eisenhaber F, Peters JM. The WD40 propeller domain of Cdh1 functions as a destruction box receptor for APC/C substrates. Mol Cell. 2005; 18:543–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2005.04.023 [PubMed]
-
147.
Brown NG, VanderLinden R, Watson ER, Qiao R, Grace CR, Yamaguchi M, Weissmann F, Frye JJ, Dube P, Ei Cho S, Actis ML, Rodrigues P, Fujii N, et al. RING E3 mechanism for ubiquitin ligation to a disordered substrate visualized for human anaphase-promoting complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015; 112:5272–79. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1504161112 [PubMed]
-
148.
Brown NG, Watson ER, Weissmann F, Jarvis MA, VanderLinden R, Grace CR, Frye JJ, Qiao R, Dube P, Petzold G, Cho SE, Alsharif O, Bao J, et al. Mechanism of polyubiquitination by human anaphase-promoting complex: RING repurposing for ubiquitin chain assembly. Mol Cell. 2014; 56:246–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.09.009 [PubMed]
-
149.
Van Voorhis VA, Morgan DO. Activation of the APC/C ubiquitin ligase by enhanced E2 efficiency. Curr Biol. 2014; 24:1556–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.05.052 [PubMed]
-
150.
Thornton BR, Ng TM, Matyskiela ME, Carroll CW, Morgan DO, Toczyski DP. An architectural map of the anaphase-promoting complex. Genes Dev. 2006; 20:449–60. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1396906 [PubMed]
-
151.
Vodermaier HC, Gieffers C, Maurer-Stroh S, Eisenhaber F, Peters JM. TPR subunits of the anaphase-promoting complex mediate binding to the activator protein CDH1. Curr Biol. 2003; 13:1459–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(03)00581-5 [PubMed]
-
152.
Buschhorn BA, Petzold G, Galova M, Dube P, Kraft C, Herzog F, Stark H, Peters JM. Substrate binding on the APC/C occurs between the coactivator Cdh1 and the processivity factor Doc1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2011; 18:6–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1979 [PubMed]
-
153.
Alfieri C, Zhang S, Barford D. Visualizing the complex functions and mechanisms of the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C). Open Biol. 2017; 7:170204. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.170204 [PubMed]
-
154.
Izawa D, Pines J. The mitotic checkpoint complex binds a second CDC20 to inhibit active APC/C. Nature. 2015; 517:631–34. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13911 [PubMed]
-
155.
Yamaguchi M, VanderLinden R, Weissmann F, Qiao R, Dube P, Brown NG, Haselbach D, Zhang W, Sidhu SS, Peters JM, Stark H, Schulman BA. cryo-EM of mitotic checkpoint complex-bound APC/C reveals reciprocal and conformational regulation of ubiquitin ligation. Mol Cell. 2016; 63:593–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.07.003 [PubMed]
-
156.
Barford D. Structural interconversions of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) regulate cell cycle transitions. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2020; 61:86–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbi.2019.11.010 [PubMed]
-
157.
Di Fiore B, Wurzenberger C, Davey NE, Pines J. The mitotic checkpoint complex requires an evolutionary conserved cassette to bind and inhibit active APC/C. Mol Cell. 2016; 64:1144–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.11.006 [PubMed]
-
158.
May KM, Paldi F, Hardwick KG. Fission yeast Apc15 stabilizes MCC-Cdc20-APC/C complexes, ensuring efficient Cdc20 ubiquitination and checkpoint arrest. Curr Biol. 2017; 27:1221–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.03.013 [PubMed]
-
159.
Luo S, Tong L. Molecular mechanism for the regulation of yeast separase by securin. Nature. 2017; 542:255–59. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature21061 [PubMed]
-
160.
Lin Z, Luo X, Yu H. Structural basis of cohesin cleavage by separase. Nature. 2016; 532:131–34. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17402 [PubMed]
-
161.
Gligoris TG, Scheinost JC, Bürmann F, Petela N, Chan KL, Uluocak P, Beckouët F, Gruber S, Nasmyth K, Löwe J. Closing the cohesin ring: structure and function of its Smc3-kleisin interface. Science. 2014; 346:963–67. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1256917 [PubMed]
-
162.
Kramer ER, Scheuringer N, Podtelejnikov AV, Mann M, Peters JM. Mitotic regulation of the APC activator proteins CDC20 and CDH1. Mol Biol Cell. 2000; 11:1555–69. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.11.5.1555 [PubMed]
-
163.
Kraft C, Herzog F, Gieffers C, Mechtler K, Hagting A, Pines J, Peters JM. Mitotic regulation of the human anaphase-promoting complex by phosphorylation. EMBO J. 2003; 22:6598–609. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/cdg627 [PubMed]
-
164.
Park HJ, Costa RH, Lau LF, Tyner AL, Raychaudhuri P. Anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome-CDH1-mediated proteolysis of the forkhead box M1 transcription factor is critical for regulated entry into S phase. Mol Cell Biol. 2008; 28:5162–71. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00387-08 [PubMed]
-
165.
Schnerch D, Yalcintepe J, Schmidts A, Becker H, Follo M, Engelhardt M, Wäsch R. Cell cycle control in acute myeloid leukemia. Am J Cancer Res. 2012; 2:508–28. [PubMed]
-
166.
Giam M, Rancati G. Aneuploidy and chromosomal instability in cancer: a jackpot to chaos. Cell Div. 2015; 10:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13008-015-0009-7 [PubMed]
-
167.
McGranahan N, Burrell RA, Endesfelder D, Novelli MR, Swanton C. Cancer chromosomal instability: therapeutic and diagnostic challenges. EMBO Rep. 2012; 13:528–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2012.61 [PubMed]
-
168.
Wang W, Zhang Y, Chen R, Tian Z, Zhai Y, Janz S, Gu C, Yang Y. Chromosomal instability and acquired drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:78234–44. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.20829 [PubMed]
-
169.
Vogelstein B, Papadopoulos N, Velculescu VE, Zhou S, Diaz LA Jr, Kinzler KW. Cancer genome landscapes. Science. 2013; 339:1546–58. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1235122 [PubMed]
-
170.
Lee AJ, Endesfelder D, Rowan AJ, Walther A, Birkbak NJ, Futreal PA, Downward J, Szallasi Z, Tomlinson IP, Howell M, Kschischo M, Swanton C. Chromosomal instability confers intrinsic multidrug resistance. Cancer Res. 2011; 71:1858–70. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3604 [PubMed]
-
171.
Ding ZY, Wu HR, Zhang JM, Huang GR, Ji DD. Expression characteristics of CDC20 in gastric cancer and its correlation with poor prognosis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014; 7:722–27. [PubMed]
-
172.
Wu WJ, Hu KS, Wang DS, Zeng ZL, Zhang DS, Chen DL, Bai L, Xu RH. CDC20 overexpression predicts a poor prognosis for patients with colorectal cancer. J Transl Med. 2013; 11:142. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-11-142 [PubMed]
-
173.
Dong S, Huang F, Zhang H, Chen Q. Overexpression of BUB1B, CCNA2, CDC20, and CDK1 in tumor tissues predicts poor survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Biosci Rep. 2019; 39:BSR20182306. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20182306 [PubMed]
-
174.
Bonaiuti P, Chiroli E, Gross F, Corno A, Vernieri C, Štefl M, Cosentino Lagomarsino M, Knop M, Ciliberto A. Cells escape an operational mitotic checkpoint through a stochastic process. Curr Biol. 2018; 28:28–37.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2017.11.031 [PubMed]
-
175.
Pan J, Chen RH. Spindle checkpoint regulates Cdc20p stability in saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 2004; 18:1439–51. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1184204 [PubMed]
-
176.
Holt JE, Lane SI, Jennings P, García-Higuera I, Moreno S, Jones KT. APC(FZR1) prevents nondisjunction in mouse oocytes by controlling meiotic spindle assembly timing. Mol Biol Cell. 2012; 23:3970–81. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E12-05-0352 [PubMed]
-
177.
Bassermann F, Frescas D, Guardavaccaro D, Busino L, Peschiaroli A, Pagano M. The Cdc14B-Cdh1-Plk1 axis controls the G2 DNA-damage-response checkpoint. Cell. 2008; 134:256–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.05.043 [PubMed]
-
178.
Wäsch R, Robbins JA, Cross FR. The emerging role of APC/CCdh1 in controlling differentiation, genomic stability and tumor suppression. Oncogene. 2010; 29:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.325 [PubMed]
-
179.
Merriman JA, Lane SI, Holt JE, Jennings PC, García-Higuera I, Moreno S, McLaughlin EA, Jones KT. Reduced chromosome cohesion measured by interkinetochore distance is associated with aneuploidy even in oocytes from young mice. Biol Reprod. 2013; 88:31. https://doi.org/10.1095/biolreprod.112.104786 [PubMed]
-
180.
Ishizawa J, Kuninaka S, Sugihara E, Naoe H, Kobayashi Y, Chiyoda T, Ueki A, Araki K, Yamamura K, Matsuzaki Y, Nakajima H, Ikeda Y, Okamoto S, Saya H. The cell cycle regulator Cdh1 controls the pool sizes of hematopoietic stem cells and mature lineage progenitors by protecting from genotoxic stress. Cancer Sci. 2011; 102:967–74. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1349-7006.2011.01884.x [PubMed]
-
181.
de Boer HR, Guerrero Llobet S, van Vugt MA. Controlling the response to DNA damage by the APC/C-Cdh1. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016; 73:949–60. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2096-7 [PubMed]
-
182.
Sigl R, Wandke C, Rauch V, Kirk J, Hunt T, Geley S. Loss of the mammalian APC/C activator FZR1 shortens G1 and lengthens S phase but has little effect on exit from mitosis. J Cell Sci. 2009; 122:4208–17. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.054197 [PubMed]
-
183.
Wei W, Ayad NG, Wan Y, Zhang GJ, Kirschner MW, Kaelin WG Jr. Degradation of the SCF component Skp2 in cell-cycle phase G1 by the anaphase-promoting complex. Nature. 2004; 428:194–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02381 [PubMed]
-
184.
Qiao X, Zhang L, Gamper AM, Fujita T, Wan Y. APC/C-Cdh1: from cell cycle to cellular differentiation and genomic integrity. Cell Cycle. 2010; 9:3904–12. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.9.19.13585 [PubMed]
-
185.
Gao D, Inuzuka H, Tseng A, Chin RY, Toker A, Wei W. Phosphorylation by Akt1 promotes cytoplasmic localization of Skp2 and impairs APCCdh1-mediated Skp2 destruction. Nat Cell Biol. 2009; 11:397–408. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1847 [PubMed]
-
186.
Sudo T, Ota Y, Kotani S, Nakao M, Takami Y, Takeda S, Saya H. Activation of Cdh1-dependent APC is required for G1 cell cycle arrest and DNA damage-induced G2 checkpoint in vertebrate cells. EMBO J. 2001; 20:6499–508. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/20.22.6499 [PubMed]
-
187.
Wäsch R, Cross FR. APC-dependent proteolysis of the mitotic cyclin Clb2 is essential for mitotic exit. Nature. 2002; 418:556–62. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00856 [PubMed]
-
188.
Hatano Y, Naoki K, Suzuki A, Ushimaru T. Positive feedback promotes mitotic exit via the APC/C-Cdh1-separase-Cdc14 axis in budding yeast. Cell Signal. 2016; 28:1545–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.07.005 [PubMed]
-
189.
Listovsky T, Oren YS, Yudkovsky Y, Mahbubani HM, Weiss AM, Lebendiker M, Brandeis M. Mammalian Cdh1/fzr mediates its own degradation. EMBO J. 2004; 23:1619–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600149 [PubMed]
-
190.
Nagai M, Shibata A, Ushimaru T. Cdh1 degradation is mediated by APC/C-Cdh1 and SCF-Cdc4 in budding yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018; 506:932–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.10.179 [PubMed]
-
191.
Fukushima H, Ogura K, Wan L, Lu Y, Li V, Gao D, Liu P, Lau AW, Wu T, Kirschner MW, Inuzuka H, Wei W. SCF-mediated Cdh1 degradation defines a negative feedback system that coordinates cell-cycle progression. Cell Rep. 2013; 4:803–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.07.031 [PubMed]
-
192.
Ishizawa J, Sugihara E, Kuninaka S, Mogushi K, Kojima K, Benton CB, Zhao R, Chachad D, Hashimoto N, Jacamo RO, Qiu Y, Yoo SY, Okamoto S, et al. FZR1 loss increases sensitivity to DNA damage and consequently promotes murine and human b-cell acute leukemia. Blood. 2017; 129:1958–68. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-07-726216 [PubMed]
-
193.
Toda K, Naito K, Mase S, Ueno M, Uritani M, Yamamoto A, Ushimaru T. APC/C-Cdh1-dependent anaphase and telophase progression during mitotic slippage. Cell Div. 2012; 7:4. https://doi.org/10.1186/1747-1028-7-4 [PubMed]
-
194.
Nagai M, Ushimaru T. Cdh1 is an antagonist of the spindle assembly checkpoint. Cell Signal. 2014; 26:2217–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.07.007 [PubMed]
-
195.
Sorensen CS, Lukas C, Kramer ER, Peters JM, Bartek J, Lukas J. Nonperiodic activity of the human anaphase-promoting complex-Cdh1 ubiquitin ligase results in continuous DNA synthesis uncoupled from mitosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2000; 20:7613–23. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.20.20.7613-7623.2000 [PubMed]
-
196.
Machida YJ, Dutta A. The APC/C inhibitor, Emi1, is essential for prevention of rereplication. Genes Dev. 2007; 21:184–94. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1495007 [PubMed]
-
197.
Wohlschlegel JA, Dwyer BT, Dhar SK, Cvetic C, Walter JC, Dutta A. Inhibition of eukaryotic DNA replication by geminin binding to Cdt1. Science. 2000; 290:2309–12. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.290.5500.2309 [PubMed]
-
198.
Ogbagabriel S, Fernando M, Waldman FM, Bose S, Heaney AP. Securin is overexpressed in breast cancer. Mod Pathol. 2005; 18:985–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.3800382 [PubMed]
-
199.
Bischoff JR, Anderson L, Zhu Y, Mossie K, Ng L, Souza B, Schryver B, Flanagan P, Clairvoyant F, Ginther C, Chan CS, Novotny M, Slamon DJ, Plowman GD. A homologue of drosophila aurora kinase is oncogenic and amplified in human colorectal cancers. EMBO J. 1998; 17:3052–65. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/17.11.3052 [PubMed]
-
200.
Mora-Santos M, Castilla C, Herrero-Ruiz J, Giráldez S, Limón-Mortés MC, Sáez C, Japón MÁ, Tortolero M, Romero F. A single mutation in securin induces chromosomal instability and enhances cell invasion. Eur J Cancer. 2013; 49:500–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2012.06.024 [PubMed]
-
201.
Wolf G, Elez R, Doermer A, Holtrich U, Ackermann H, Stutte HJ, Altmannsberger HM, Rübsamen-Waigmann H, Strebhardt K. Prognostic significance of polo-like kinase (PLK) expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene. 1997; 14:543–49. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1200862 [PubMed]
-
202.
Knecht R, Oberhauser C, Strebhardt K. PLK (polo-like kinase), a new prognostic marker for oropharyngeal carcinomas. Int J Cancer. 2000; 89:535–36. [PubMed]
-
203.
King SI, Purdie CA, Bray SE, Quinlan PR, Jordan LB, Thompson AM, Meek DW. Immunohistochemical detection of polo-like kinase-1 (PLK1) in primary breast cancer is associated with TP53 mutation and poor clinical outcom. Breast Cancer Res. 2012; 14:R40. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr3136 [PubMed]
-
204.
Lens SM, Voest EE, Medema RH. Shared and separate functions of polo-like kinases and aurora kinases in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010; 10:825–41. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc2964 [PubMed]
-
205.
Kotani S, Tugendreich S, Fujii M, Jorgensen PM, Watanabe N, Hoog C, Hieter P, Todokoro K. PKA and MPF-activated polo-like kinase regulate anaphase-promoting complex activity and mitosis progression. Mol Cell. 1998; 1:371–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80037-4 [PubMed]
-
206.
Rudner AD, Murray AW. Phosphorylation by Cdc28 activates the Cdc20-dependent activity of the anaphase-promoting complex. J Cell Biol. 2000; 149:1377–90. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.149.7.1377 [PubMed]
-
207.
Eckerdt F, Strebhardt K. Polo-like kinase 1: target and regulator of anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome-dependent proteolysis. Cancer Res. 2006; 66:6895–98. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-0358 [PubMed]
-
208.
Lane HA, Nigg EA. Antibody microinjection reveals an essential role for human polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) in the functional maturation of mitotic centrosomes. J Cell Biol. 1996; 135:1701–13. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.135.6.1701 [PubMed]
-
209.
Abrieu A, Brassac T, Galas S, Fisher D, Labbé JC, Dorée M. The polo-like kinase Plx1 is a component of the MPF amplification loop at the G2/m-phase transition of the cell cycle in xenopus eggs. J Cell Sci. 1998; 111:1751–57. [PubMed]
-
210.
Sumara I, Giménez-Abián JF, Gerlich D, Hirota T, Kraft C, de la Torre C, Ellenberg J, Peters JM. Roles of polo-like kinase 1 in the assembly of functional mitotic spindles. Curr Biol. 2004; 14:1712–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2004.09.049 [PubMed]
-
211.
Seong YS, Kamijo K, Lee JS, Fernandez E, Kuriyama R, Miki T, Lee KS. A spindle checkpoint arrest and a cytokinesis failure by the dominant-negative polo-box domain of Plk1 in U-2 OS cells. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:32282–93. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M202602200 [PubMed]
-
212.
Liu X, Erikson RL. Polo-like kinase (Plk)1 depletion induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003; 100:5789–94. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1031523100 [PubMed]
-
213.
Li Z, Liu J, Li J, Kong Y, Sandusky G, Rao X, Liu Y, Wan J, Liu X. Polo-like kinase 1 (Plk1) overexpression enhances ionizing radiation-induced cancer formation in mice. J Biol Chem. 2017; 292:17461–72. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M117.810960 [PubMed]
-
214.
Bolanos-Garcia VM. Assessment of the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint (SAC) as the target of anticancer therapies. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2009; 9:131–41. https://doi.org/10.2174/156800909787580980 [PubMed]
-
215.
Li JJ, Weroha SJ, Lingle WL, Papa D, Salisbury JL, Li SA. Estrogen mediates aurora-a overexpression, centrosome amplification, chromosomal instability, and breast cancer in female ACI rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004; 101:18123–28. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0408273101 [PubMed]
-
216.
Li D, Zhu J, Firozi PF, Abbruzzese JL, Evans DB, Cleary K, Friess H, Sen S. Overexpression of oncogenic STK15/BTAK/aurora a kinase in human pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2003; 9:991–97. [PubMed]
-
217.
Zhang H, Chen X, Jin Y, Liu B, Zhou L. Overexpression of aurora-a promotes laryngeal cancer progression by enhancing invasive ability and chromosomal instability. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 269:607–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-011-1629-4 [PubMed]
-
218.
Anand S, Penrhyn-Lowe S, Venkitaraman AR. AURORA-a amplification overrides the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint, inducing resistance to taxol. Cancer Cell. 2003; 3:51–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1535-6108(02)00235-0 [PubMed]
-
219.
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Lees E, Seghezzi W. AuroraA overexpression overrides the mitotic spindle checkpoint triggered by nocodazole, a microtubule destabilizer. Oncogene. 2003; 22:8293–301. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1206873 [PubMed]
-
220.
Andreassen PR, Margolis RL. Microtubule dependency of p34cdc2 inactivation and mitotic exit in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol. 1994; 127:789–802. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.127.3.789 [PubMed]
-
221.
Sinha D, Duijf PH, Khanna KK. Mitotic slippage: an old tale with a new twist. Cell Cycle. 2019; 18:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2018.1559557 [PubMed]
-
222.
Rosenbluth JM, Mays DJ, Pino MF, Tang LJ, Pietenpol JA. A gene signature-based approach identifies mTOR as a regulator of p73. Mol Cell Biol. 2008; 28:5951–64. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00305-08 [PubMed]
-
223.
Tomasini R, Mak TW, Melino G. The impact of p53 and p73 on aneuploidy and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2008; 18:244–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2008.03.003 [PubMed]
-
224.
Katayama H, Wang J, Treekitkarnmongkol W, Kawai H, Sasai K, Zhang H, Wang H, Adams HP, Jiang S, Chakraborty SN, Suzuki F, Arlinghaus RB, Liu J, et al. Aurora kinase-a inactivates DNA damage-induced apoptosis and spindle assembly checkpoint response functions of p73. Cancer Cell. 2012; 21:196–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2011.12.025 [PubMed]
-
225.
Hauf S, Cole RW, LaTerra S, Zimmer C, Schnapp G, Walter R, Heckel A, van Meel J, Rieder CL, Peters JM. The small molecule hesperadin reveals a role for aurora B in correcting kinetochore-microtubule attachment and in maintaining the spindle assembly checkpoint. J Cell Biol. 2003; 161:281–94. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200208092 [PubMed]
-
226.
Tsuda Y, Iimori M, Nakashima Y, Nakanishi R, Ando K, Ohgaki K, Kitao H, Saeki H, Oki E, Maehara Y. Mitotic slippage and the subsequent cell fates after inhibition of aurora B during tubulin-binding agent-induced mitotic arrest. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:16762. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-17002-z [PubMed]
-
227.
Xia J, Franqui Machin R, Gu Z, Zhan F. Role of NEK2A in human cancer and its therapeutic potentials. Biomed Res Int. 2015; 2015:862461. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/862461 [PubMed]
-
228.
Cervenka I, Valnohova J, Bernatik O, Harnos J, Radsetoulal M, Sedova K, Hanakova K, Potesil D, Sedlackova M, Salasova A, Steinhart Z, Angers S, Schulte G, et al. Dishevelled is a NEK2 kinase substrate controlling dynamics of centrosomal linker proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2016; 113:9304–09. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1608783113 [PubMed]
-
229.
Park J, Rhee K. NEK2 phosphorylation antagonizes the microtubule stabilizing activity of centrobin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013; 431:302–08. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.12.106 [PubMed]
-
230.
Guo HQ, Gao M, Ma J, Xiao T, Zhao LL, Gao Y, Pan QJ. Analysis of the cellular centrosome in fine-needle aspirations of the breast. Breast Cancer Res. 2007; 9:R48. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr1752 [PubMed]
-
231.
Wang S, Li W, Liu N, Zhang F, Liu H, Liu F, Liu J, Zhang T, Niu Y. Nek2A contributes to tumorigenic growth and possibly functions as potential therapeutic target for human breast cancer. J Cell Biochem. 2012; 113:1904–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.24059 [PubMed]
-
232.
Sun Y, Liu X, Ng-Eaton E, Lodish HF, Weinberg RA. SnoN and ski protooncoproteins are rapidly degraded in response to transforming growth factor beta signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1999; 96:12442–47. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.22.12442 [PubMed]
-
233.
Stroschein SL, Wang W, Zhou S, Zhou Q, Luo K. Negative feedback regulation of TGF-beta signaling by the SnoN oncoprotein. Science. 1999; 286:771–74. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.286.5440.771 [PubMed]
-
234.
Miettinen PJ, Ebner R, Lopez AR, Derynck R. TGF-beta induced transdifferentiation of mammary epithelial cells to mesenchymal cells: involvement of type I receptors. J Cell Biol. 1994; 127:2021–36. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.127.6.2021 [PubMed]
-
235.
Li X, Diao Z, Ding J, Liu R, Wang L, Huang W, Liu W. The downregulation of SnoN expression in human renal proximal tubule epithelial cells under high-glucose conditions is mediated by an increase in Smurf2 expression through TGF-β1 signaling. Int J Mol Med. 2016; 37:415–22. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2015.2448 [PubMed]
-
236.
Caja F, Vannucci L. TGFβ: a player on multiple fronts in the tumor microenvironment. J Immunotoxicol. 2015; 12:300–07. https://doi.org/10.3109/1547691X.2014.945667 [PubMed]
-
237.
Band AM, Laiho M. SnoN oncoprotein enhances estrogen receptor-α transcriptional activity. Cell Signal. 2012; 24:922–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.12.015 [PubMed]
-
238.
Korver W, Roose J, Clevers H. The winged-helix transcription factor trident is expressed in cycling cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997; 25:1715–19. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/25.9.1715 [PubMed]
-
239.
Ye H, Kelly TF, Samadani U, Lim L, Rubio S, Overdier DG, Roebuck KA, Costa RH. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/fork head homolog 11 is expressed in proliferating epithelial and mesenchymal cells of embryonic and adult tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1997; 17:1626–41. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.17.3.1626 [PubMed]
-
240.
Wang IC, Chen YJ, Hughes D, Petrovic V, Major ML, Park HJ, Tan Y, Ackerson T, Costa RH. Forkhead box M1 regulates the transcriptional network of genes essential for mitotic progression and genes encoding the SCF (Skp2-Cks1) ubiquitin ligase. Mol Cell Biol. 2005; 25:10875–94. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.25.24.10875-10894.2005 [PubMed]
-
241.
Ganoth D, Bornstein G, Ko TK, Larsen B, Tyers M, Pagano M, Hershko A. The cell-cycle regulatory protein Cks1 is required for SCF(Skp2)-mediated ubiquitinylation of p27. Nat Cell Biol. 2001; 3:321–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/35060126 [PubMed]
-
242.
Li LQ, Pan D, Chen H, Zhang L, Xie WJ. F-box protein FBXL2 inhibits gastric cancer proliferation by ubiquitin-mediated degradation of forkhead box M1. FEBS Lett. 2016; 590:445–52. https://doi.org/10.1002/1873-3468.12071 [PubMed]
-
243.
Jeffery JM, Kalimutho M, Johansson P, Cardenas DG, Kumar R, Khanna KK. FBXO31 protects against genomic instability by capping FOXM1 levels at the G2/M transition. Oncogene. 2017; 36:1012–22. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.268 [PubMed]
-
244.
Wang X, Krupczak-Hollis K, Tan Y, Dennewitz MB, Adami GR, Costa RH. Increased hepatic forkhead box M1B (FoxM1B) levels in old-aged mice stimulated liver regeneration through diminished p27Kip1 protein levels and increased Cdc25B expression. J Biol Chem. 2002; 277:44310–16. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M207510200 [PubMed]
-
245.
Fung TK, Poon RY. A roller coaster ride with the mitotic cyclins. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2005; 16:335–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2005.02.014 [PubMed]
-
246.
Laoukili J, Kooistra MR, Brás A, Kauw J, Kerkhoven RM, Morrison A, Clevers H, Medema RH. FoxM1 is required for execution of the mitotic programme and chromosome stability. Nat Cell Biol. 2005; 7:126–36. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1217 [PubMed]
-
247.
Xie Q, Wu Q, Mack SC, Yang K, Kim L, Hubert CG, Flavahan WA, Chu C, Bao S, Rich JN. CDC20 maintains tumor initiating cells. Oncotarget. 2015; 6:13241–54. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3676 [PubMed]
-
248.
Nicolau-Neto P, Palumbo A, De Martino M, Esposito F, de Almeida Simão T, Fusco A, Nasciutti LE, Meireles Da Costa N, Ribeiro Pinto LF. UBE2C is a transcriptional target of the cell cycle regulator FOXM1. Genes (Basel). 2018; 9:188. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9040188 [PubMed]
-
249.
Laoukili J, Alvarez-Fernandez M, Stahl M, Medema RH. FoxM1 is degraded at mitotic exit in a Cdh1-dependent manner. Cell Cycle. 2008; 7:2720–26. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.7.17.6580 [PubMed]
-
250.
Jiang L, Cao XC, Cao JG, Liu F, Quan MF, Sheng XF, Ren KQ. Casticin induces ovarian cancer cell apoptosis by repressing FoxM1 through the activation of FOXO3a. Oncol Lett. 2013; 5:1605–10. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2013.1258 [PubMed]
-
251.
Wen N, Wang Y, Wen L, Zhao SH, Ai ZH, Wang Y, Wu B, Lu HX, Yang H, Liu WC, Li Y. Overexpression of FOXM1 predicts poor prognosis and promotes cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Transl Med. 2014; 12:134. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-5876-12-134 [PubMed]
-
252.
Jaiswal N, Chakraborty S, Nag A. Biology of FOXM1 and its Emerging Role in Cancer Therapy. Journal of Proteins and Proteomics. 2014; 5:1–24.
-
253.
Wang K, Zhu X, Zhang K, Zhu L, Zhou F. FoxM1 inhibition enhances chemosensitivity of docetaxel-resistant A549 cells to docetaxel via activation of JNK/mitochondrial pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2016; 48:804–09. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmw072 [PubMed]
-
254.
Dai B, Kang SH, Gong W, Liu M, Aldape KD, Sawaya R, Huang S. Aberrant FoxM1B expression increases matrix metalloproteinase-2 transcription and enhances the invasion of glioma cells. Oncogene. 2007; 26:6212–19. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1210443 [PubMed]
-
255.
Halasi M, Gartel AL. Suppression of FOXM1 sensitizes human cancer cells to cell death induced by DNA-damage. PLoS One. 2012; 7:e31761. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031761 [PubMed]
-
256.
Pandit B, Gartel AL. FoxM1 knockdown sensitizes human cancer cells to proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis but not to autophagy. Cell Cycle. 2011; 10:3269–73. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.10.19.17735 [PubMed]
-
257.
Jin C, Liu Z, Li Y, Bu H, Wang Y, Xu Y, Qiu C, Yan S, Yuan C, Li R, Diao N, Zhang Z, Wang X, et al. PCNA-associated factor P15PAF, targeted by FOXM1, predicts poor prognosis in high-grade serous ovarian cancer patients. Int J Cancer. 2018; 143:2973–84. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31800 [PubMed]
-
258.
Wang X, Chen D, Gao J, Long H, Zha H, Zhang A, Shu C, Zhou L, Yang F, Zhu B, Wu W. Centromere protein U expression promotes non-small-cell lung cancer cell proliferation through FOXM1 and predicts poor survival. Cancer Manag Res. 2018; 10:6971–84. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S182852 [PubMed]
-
259.
Xu X, Huang S, Zhang B, Huang F, Chi W, Fu J, Wang G, Li S, Jiang Q, Zhang C. DNA replication licensing factor Cdc6 and Plk4 kinase antagonistically regulate centrosome duplication via sas-6. Nat Commun. 2017; 8:15164. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15164 [PubMed]
-
260.
Tanaka T, Knapp D, Nasmyth K. Loading of an mcm protein onto DNA replication origins is regulated by Cdc6p and CDKs. Cell. 1997; 90:649–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)80526-7 [PubMed]
-
261.
Donovan S, Harwood J, Drury LS, Diffley JF. Cdc6p-dependent loading of mcm proteins onto pre-replicative chromatin in budding yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997; 94:5611–16. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.11.5611 [PubMed]
-
262.
Coleman TR, Carpenter PB, Dunphy WG. The xenopus Cdc6 protein is essential for the initiation of a single round of DNA replication in cell-free extracts. Cell. 1996; 87:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81322-7 [PubMed]
-
263.
Petersen BO, Wagener C, Marinoni F, Kramer ER, Melixetian M, Lazzerini Denchi E, Gieffers C, Matteucci C, Peters JM, Helin K. Cell cycle- and cell growth-regulated proteolysis of mammalian CDC6 is dependent on APC-CDH1. Genes Dev. 2000; 14:2330–43. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.832500 [PubMed]
-
264.
Li A, Blow JJ. Cdt1 downregulation by proteolysis and geminin inhibition prevents DNA re-replication in xenopus. EMBO J. 2005; 24:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600520 [PubMed]
-
265.
Mailand N, Diffley JF. CDKs promote DNA replication origin licensing in human cells by protecting Cdc6 from APC/c-dependent proteolysis. Cell. 2005; 122:915–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.013 [PubMed]
-
266.
Elsasser S, Chi Y, Yang P, Campbell JL. Phosphorylation controls timing of Cdc6p destruction: a biochemical analysis. Mol Biol Cell. 1999; 10:3263–77. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.10.10.3263 [PubMed]
-
267.
Drury LS, Perkins G, Diffley JF. The cyclin-dependent kinase Cdc28p regulates distinct modes of Cdc6p proteolysis during the budding yeast cell cycle. Curr Biol. 2000; 10:231–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0960-9822(00)00355-9 [PubMed]
-
268.
Neves H, Kwok HF. In sickness and in health: the many roles of the minichromosome maintenance proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2017; 1868:295–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2017.06.001 [PubMed]
-
269.
Stead BE, Sorbara CD, Brandl CJ, Davey MJ. ATP binding and hydrolysis by Mcm2 regulate DNA binding by mcm complexes. J Mol Biol. 2009; 391:301–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2009.06.038 [PubMed]
-
270.
Cortez D, Glick G, Elledge SJ. Minichromosome maintenance proteins are direct targets of the ATM and ATR checkpoint kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004; 101:10078–83. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0403410101 [PubMed]
-
271.
Liang C, Stillman B. Persistent initiation of DNA replication and chromatin-bound MCM proteins during the cell cycle in cdc6 mutants. Genes Dev. 1997; 11:3375–86. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.11.24.3375 [PubMed]
-
272.
Going JJ, Keith WN, Neilson L, Stoeber K, Stuart RC, Williams GH. Aberrant expression of minichromosome maintenance proteins 2 and 5, and ki-67 in dysplastic squamous oesophageal epithelium and barrett’s mucosa. Gut. 2002; 50:373–77. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.50.3.373 [PubMed]
-
273.
Karakaidos P, Taraviras S, Vassiliou LV, Zacharatos P, Kastrinakis NG, Kougiou D, Kouloukoussa M, Nishitani H, Papavassiliou AG, Lygerou Z, Gorgoulis VG. Overexpression of the replication licensing regulators hCdt1 and hCdc6 characterizes a subset of non-small-cell lung carcinomas: synergistic effect with mutant p53 on tumor growth and chromosomal instability—evidence of E2F-1 transcriptional control over hCdt1. Am J Pathol. 2004; 165:1351–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63393-7 [PubMed]
-
274.
Petropoulou C, Kotantaki P, Karamitros D, Taraviras S. Cdt1 and geminin in cancer: markers or triggers of Malignant transformation? Front Biosci. 2008; 13:4485–94. https://doi.org/10.2741/3018 [PubMed]
-
275.
Mahadevappa R, Neves H, Yuen SM, Bai Y, McCrudden CM, Yuen HF, Wen Q, Zhang SD, Kwok HF. The prognostic significance of Cdc6 and Cdt1 in breast cancer. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:985. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-00998-9 [PubMed]
-
276.
Gou K, Liu J, Feng X, Li H, Yuan Y, Xing C. Expression of minichromosome maintenance proteins (MCM) and cancer prognosis: a meta-analysis. J Cancer. 2018; 9:1518–26. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.22691 [PubMed]
-
277.
Feng CJ, Li HJ, Li JN, Lu YJ, Liao GQ. Expression of Mcm7 and Cdc6 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and precancerous lesions. Anticancer Res. 2008; 28:3763–69. [PubMed]
-
278.
Kim GS, Lee I, Kim JH, Hwang DS. The replication protein Cdc6 suppresses centrosome over-duplication in a manner independent of its ATPase activity. Mol Cells. 2017; 40:925–34. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.0191 [PubMed]
-
279.
Ballabeni A, Zamponi R, Caprara G, Melixetian M, Bossi S, Masiero L, Helin K. Human CDT1 associates with CDC7 and recruits CDC45 to chromatin during S phase. J Biol Chem. 2009; 284:3028–36. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M803609200 [PubMed]
-
280.
Vaziri C, Saxena S, Jeon Y, Lee C, Murata K, Machida Y, Wagle N, Hwang DS, Dutta A. A p53-dependent checkpoint pathway prevents rereplication. Mol Cell. 2003; 11:997–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(03)00099-6 [PubMed]
-
281.
McGarry TJ, Kirschner MW. Geminin, an inhibitor of DNA replication, is degraded during mitosis. Cell. 1998; 93:1043–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81209-x [PubMed]
-
282.
Rape M, Reddy SK, Kirschner MW. The processivity of multiubiquitination by the APC determines the order of substrate degradation. Cell. 2006; 124:89–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2005.10.032 [PubMed]
-
283.
Zhang L, Cai M, Gong Z, Zhang B, Li Y, Guan L, Hou X, Li Q, Liu G, Xue Z, Yang MH, Ye J, Chin YE, You H. Geminin facilitates FoxO3 deacetylation to promote breast cancer cell metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2017; 127:2159–75. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI90077 [PubMed]
-
284.
Sundara Rajan S, Hanby AM, Horgan K, Thygesen HH, Speirs V. The potential utility of geminin as a predictive biomarker in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014; 143:91–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-013-2786-5 [PubMed]
-
285.
Joshi S, Watkins J, Gazinska P, Brown JP, Gillett CE, Grigoriadis A, Pinder SE. Digital imaging in the immunohistochemical evaluation of the proliferation markers Ki67, MCM2 and geminin, in early breast cancer, and their putative prognostic value. BMC Cancer. 2015; 15:546. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-015-1531-3 [PubMed]
-
286.
Park YY, Ahn JH, Cho MG, Lee JH. ATP depletion during mitotic arrest induces mitotic slippage and APC/CCdh1-dependent cyclin B1 degradation. Exp Mol Med. 2018; 50:46. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-018-0069-2 [PubMed]
-
287.
Wirth KG, Ricci R, Giménez-Abián JF, Taghybeeglu S, Kudo NR, Jochum W, Vasseur-Cognet M, Nasmyth K. Loss of the anaphase-promoting complex in quiescent cells causes unscheduled hepatocyte proliferation. Genes Dev. 2004; 18:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.285404 [PubMed]
-
288.
Sánchez-Pérez T, Medema RH, López-Rivas A. Delaying mitotic exit downregulates FLIP expression and strongly sensitizes tumor cells to TRAIL. Oncogene. 2015; 34:661–69. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.601 [PubMed]
-
289.
Liu X, Chen Y, Li Y, Petersen RB, Huang K. Targeting mitosis exit: a brake for cancer cell proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2019; 1871:179–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2018.12.007 [PubMed]
-
290.
Riffell JL, Zimmerman C, Khong A, McHardy LM, Roberge M. Effects of chemical manipulation of mitotic arrest and slippage on cancer cell survival and proliferation. Cell Cycle. 2009; 8:3025–38. [PubMed]
-
291.
Zhu Y, Zhou Y, Shi J. Post-slippage multinucleation renders cytotoxic variation in anti-mitotic drugs that target the microtubules or mitotic spindle. Cell Cycle. 2014; 13:1756–64. https://doi.org/10.4161/cc.28672 [PubMed]
-
292.
Ohashi A. Different cell fates after mitotic slippage: from aneuploidy to polyploidy. Mol Cell Oncol. 2015; 3:e1088503. https://doi.org/10.1080/23723556.2015.1088503 [PubMed]
-
293.
Sudo T, Nitta M, Saya H, Ueno NT. Dependence of paclitaxel sensitivity on a functional spindle assembly checkpoint. Cancer Res. 2004; 64:2502–08. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-2013 [PubMed]
-
294.
Yasuhira S, Shibazaki M, Nishiya M, Maesawa C. Paclitaxel-induced aberrant mitosis and mitotic slippage efficiently lead to proliferative death irrespective of canonical apoptosis and p53. Cell Cycle. 2016; 15:3268–77. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2016.1242537 [PubMed]
-
295.
Choi M, Min YH, Pyo J, Lee CW, Jang CY, Kim JE. TC Mps1 12, a novel Mps1 inhibitor, suppresses the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the accumulation of chromosomal instability. Br J Pharmacol. 2017; 174:1810–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13782 [PubMed]
-
296.
Wang S, Zhang M, Liang D, Sun W, Zhang C, Jiang M, Liu J, Li J, Li C, Yang X, Zhou X. Molecular design and anticancer activities of small-molecule monopolar spindle 1 inhibitors: a medicinal chemistry perspective. Eur J Med Chem. 2019; 175:247–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.04.047 [PubMed]
-
297.
Peschiaroli A, Dorrello NV, Guardavaccaro D, Venere M, Halazonetis T, Sherman NE, Pagano M. SCFbetaTrCP-mediated degradation of claspin regulates recovery from the DNA replication checkpoint response. Mol Cell. 2006; 23:319–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.06.013 [PubMed]
-
298.
Mailand N, Bekker-Jensen S, Bartek J, Lukas J. Destruction of claspin by SCFbetaTrCP restrains Chk1 activation and facilitates recovery from genotoxic stress. Mol Cell. 2006; 23:307–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2006.06.016 [PubMed]
-
299.
Mamely I, van Vugt MA, Smits VA, Semple JI, Lemmens B, Perrakis A, Medema RH, Freire R. Polo-like kinase-1 controls proteasome-dependent degradation of claspin during checkpoint recovery. Curr Biol. 2006; 16:1950–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2006.08.026 [PubMed]
-
300.
Linke C, Klipp E, Lehrach H, Barberis M, Krobitsch S. Fkh1 and Fkh2 associate with Sir2 to control CLB2 transcription under normal and oxidative stress conditions. Front Physiol. 2013; 4:173. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2013.00173 [PubMed]
-
301.
Magnuson T, Epstein CJ. Oligosyndactyly: a lethal mutation in the mouse that results in mitotic arrest very early in development. Cell. 1984; 38:823–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(84)90277-0 [PubMed]
-
302.
Melloy PG. The anaphase-promoting complex: a key mitotic regulator associated with somatic mutations occurring in cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2020; 59:189–202. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22820 [PubMed]
-
303.
Turnell AS, Stewart GS, Grand RJ, Rookes SM, Martin A, Yamano H, Elledge SJ, Gallimore PH. The APC/C and CBP/p300 cooperate to regulate transcription and cell-cycle progression. Nature. 2005; 438:690–95. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04151 [PubMed]
-
304.
Yamaguchi M, Yu S, Qiao R, Weissmann F, Miller DJ, VanderLinden R, Brown NG, Frye JJ, Peters JM, Schulman BA. Structure of an APC3-APC16 complex: insights into assembly of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome. J Mol Biol. 2015; 427:1748–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2014.11.020 [PubMed]
-
305.
Park KH, Choi SE, Eom M, Kang Y. Downregulation of the anaphase-promoting complex (APC)7 in invasive ductal carcinomas of the breast and its clinicopathologic relationships. Breast Cancer Res. 2005; 7:R238–47. https://doi.org/10.1186/bcr978 [PubMed]
-
306.
Ajeawung NF, Nguyen TT, Lu L, Kucharski TJ, Rousseau J, Molidperee S, Atienza J, Gamache I, Jin W, Plon SE, Lee BH, Teodoro JG, Wang LL, Campeau PM. Mutations in ANAPC1, encoding a scaffold subunit of the anaphase-promoting complex, cause rothmund-thomson syndrome type 1. Am J Hum Genet. 2019; 105:625–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2019.06.011 [PubMed]
-
307.
Drouet Y, Treilleux I, Viari A, Léon S, Devouassoux-Shisheboran M, Voirin N, de la Fouchardière C, Manship B, Puisieux A, Lasset C, Moyret-Lalle C. Integrated analysis highlights APC11 protein expression as a likely new independent predictive marker for colorectal cancer. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:7386. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25631-1 [PubMed]